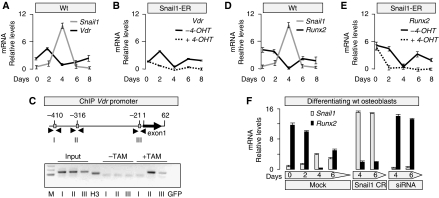
Figure 5.
Snail1 directly regulates Vdr and Runx2 expression during osteoblast differentiation in culture (A) The levels of Snail1 and Vdr expression are inversely correlated during osteoblast differentiation. (B) Sustained activation of Snail1 after 4-OHT administration maintains low Vdr expression. (C) Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assays carried out on osteoblasts differentiated from Snail1-ER transgenic mice confirm that Snail1 only binds to boxes II and III in the Vdr promoter on tamoxifen administration. M, fragment length markers; input material was tested for each primer set (boxes I, II and III); H3, positive control of the immunoprecipitate, the sample was immunoprecipitated with anti-H3 antibody and amplified with Gapdh primers; GFP, negative control of the immunoprecipitate, the sample was immunoprecipitated with anti-GFP antibody and amplified with Gapdh primers. (D, E) The levels of Snail1 and Runx2 expression are also inversely correlated during osteoblast differentiation, and similarly, sustained Snail1 activation maintains Runx2 expression inhibited. (F) When osteoblast primary cultures were transfected with a plasmid containing the coding region of Snail1 (Snail1 CR), Runx2 expression was very weak, whereas transfection with a Snail1 siRNA led to stable and strong Runx2 expression.