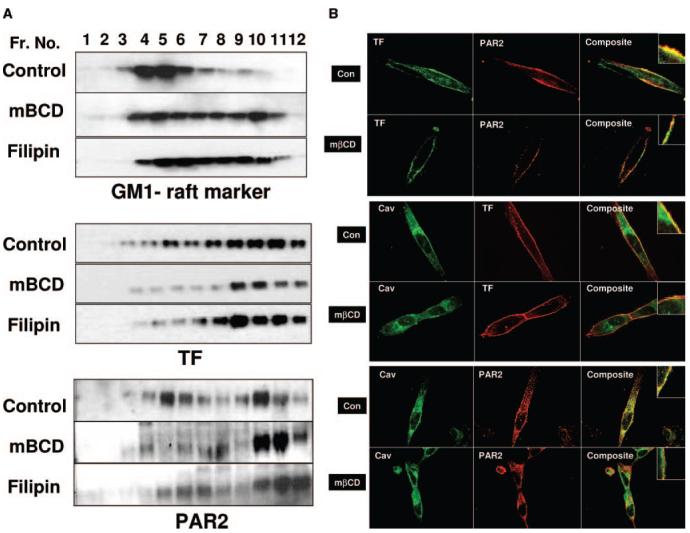
Figure 2.
Effects of membrane cholesterol depletion/modification on TF and PAR2 association with lipid rafts and caveolae. MDA-MB-231 cells cultured in T-75 flask (A) or chambered-glass slides (B) were treated with a control vehicle or mβCD (10 mmol/L) for 1 hour, or filipin (5 μg/mL) for 15 minutes. A, Cells were lysed in 1% Triton X-100, subjected sucrose gradient centrifugation; 10 μg of protein from each fraction were separated on SDS-PAGE for immunoblotting with polyclonal antibodies to TF and PAR2, and HRP-conjugated cholera toxin (as a raft marker). Fractions are labeled from the top to the bottom of the sucrose gradient. GM1 and PAR2 panels for control vehicle-treated cells in this figure and Figure 1A were the same. B, Immunofluorescence microscopy of TF, PAR2, and caveolin-1. MDA-MB-231 cells were fixed; nonpermeabilized (top panel) or permeabilized (middle and bottom panels) cells were stained with polyclonal or monoclonal antibodies to TF, PAR2, and caveolin-1. Right panels depict overlay of images, and yellow in the panel represents colocalization of TF and PAR2 with caveolin-1. The images represent single X-Y-plane of a mid-section from z-stacks.