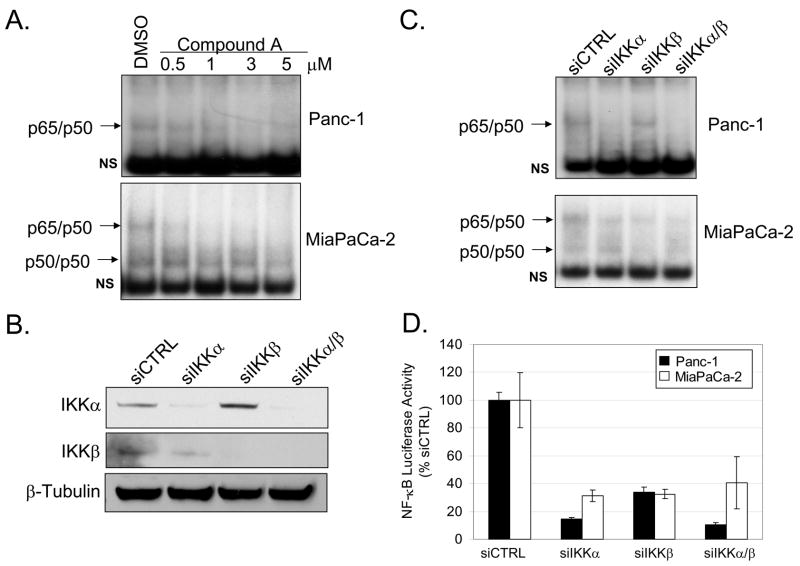
Figure 4. IKK is required for constitutive NF-κB activation.
(A) Panc-1 and MiaPaCa-2 cells were treated with DMSO or 0.5, 1, 3, and 5μM of IKKβ inhibitor (Compound A) for 24 hours. Nuclear extracts were harvested and EMSA was performed using 32P-labeled NF-κB-specific probe. Arrows indicate NF-κB complexes as determined by supershift analysis in Fig. 1A. Non-specific binding is indicated with NS. (B) Panc-1 cells were transiently transfected with 100nM siRNA targeted against IKKα, IKKβ, combined IKKα/β, and siCTRL for 48 hours. Cytoplasmic extracts were harvested from cells transfected with siRNA as described above. Extracts were separated by SDS-PAGE and immunoblots were performed using the specified antibodies. (C) EMSA was performed on nuclear extracts harvested from cells transfected with siRNA as described above. (D) Panc-1 and MiaPaCa-2 cells were transfected with siRNA as described above for 24 hours. Cells were subsequently transfected with 3X-NF-κB and renilla luciferase reporter constructs for 24 hours. Luciferase activity was measured in triplicate and indicated as % activity relative to siCTRL. Reporter activity from cells transfected with IKK siRNA were all found to be significantly different relative to siCTRL.