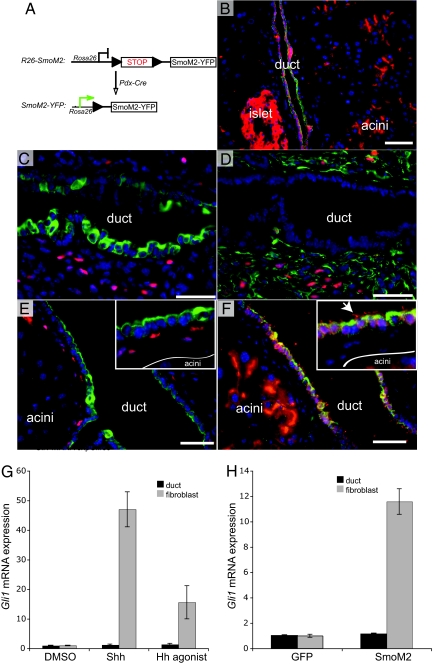
Fig. 1.
Pancreatic epithelium is not competent to transduce Hh signal downstream of SmoM2. (A) Schematic of the R26-SmoM2 targeted allele and PdxCre transgene. PdxCre mediates Loxp recombination, removing the stop cassette to result in expression of SmoM2-YFP within the pancreatic epithelium. Fusion of YFP to the C terminus of SmoM2 allows immunofluorescence detection of the transgene and thus Cre activity. (B) Stochastic expression of SmoM2-YFP (red) within the pancreatic epithelium, including ducts (CK19, green), acini, and islet. (C) β-galactosidase immunoreactivity (red) in periductal mesenchyme of Ptc-LacZ transgenic animal (ductal cells express CK19, green). (D) β-galactosidase immunoreactivity (red) in periductal mesenchyme (vimentin, green) of Ptc-LacZ mice (adjacent, serial section to C). (E) β-galactosidase immunoreactivity (red) in periductal mesenchyme of PdxCre;SmoM2;PtcLacZ animal (ductal cells express CK19, green). (F) SmoM2-YFP (red) is expressed by ductal cells (CK19, green) and acinar epithelium (adjacent, serial section to E). Note that SmoM2 accumulates in the primary cilia (arrow) of interlobular ducts. No SmoM2 is detected in the periductal mesenchyme. These images are representative of analysis from 3 animals per genotype. (Scale bars, 50 μm.) (G) Both Shh (rShh, 200 ng/ml) and Hh agonist (1 μg/ml) fail to induce the Hh target gene Gli1 in PDECs, but strongly activate the pathway in pancreatic fibroblasts. (H) SmoM2 over-expression up-regulates Gli1 mRNA levels in pancreatic fibroblasts, but not in PDEC.