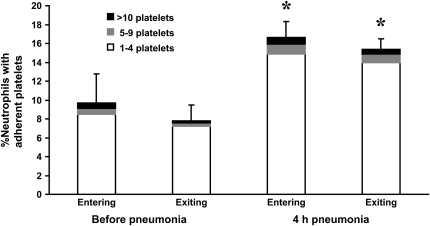
Figure 7.
The percentage of circulating neutrophils that bound platelets in the venous and arterial blood before and at 4 h after instillation of E. coli. This percentage increased approximately two-fold during E. coli pneumonia, and this change was due to an increase in the percentage of neutrophils binding 1–4 platelets. No increase was observed in the percentage of neutrophils binding 5–9 or more than 10 platelets. This increase occurred in both venous and arterial blood samples. There was no significant difference in the percentage of neutrophils that bound platelets in the venous compared to the arterial blood samples before pneumonia or at 4 h after instillation. * Significantly greater than the percentage of neutrophils that bound platelets before pneumonia, p < 0.05.