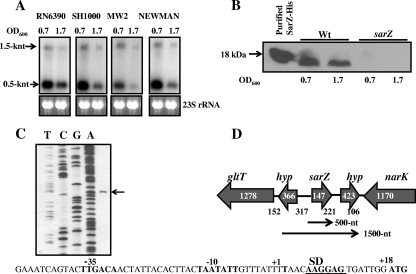
FIG. 2.
Transcription, expression, and promoter analysis of the sarZ gene in S. aureus. (A) Northern analysis of the sarZ transcripts in the different wild-type strains at various phases of growth (an OD600 of 0.7 is approximately the early exponential phase of growth, and an OD600 of 1.7 is approximately the postexponential phase of growth). The blots were probed with 500-bp sarZ DNA fragments containing the entire ORF of the sarZ gene. The region of 23S rRNA of the ethidium bromide-stained gel used for blotting is also shown as a loading control. (B) Cell extracts of the RN6390 strain were immunoblotted onto nitrocellulose and probed with anti-SarZ polyclonal antibodies. A purified His tag fusion of SarZ was loaded as a positive control. Wt, wild type. (C) Primer extension of the sarZ transcript with total RNA isolated from the wild-type RN6390 at the exponential phase of growth. The nucleotide sequence with the predicted promoter region of the sarZ ribosome-binding site (SD) and the translational start codon (ATG) are indicated. (D) Location of the sarZ gene (SA2174) on the S. aureus chromosome. The sarZ gene and the other ORFs in its vicinity are depicted. The number within each ORF indicates the size of the gene (in bp), and the number below the junction of two neighboring genes is the intergenic distance (in bp) between them. hyp, hypothetical ORF with unknown function. The location of a 500-nt transcript is mapped based on primer extension results, whereas the origin of the 1,500-nt transcript is hypothetical.