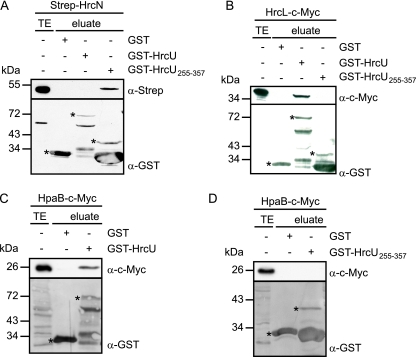
FIG. 8.
Interaction studies with HrcN and HrcL. (A) HrcN binds to the C-terminal domain of HrcU. GST, GST-HrcU and GST-HrcU255-357 were immobilized on glutathione-Sepharose and incubated with an E. coli lysate containing Strep-HrcN. Total cell extracts (TE) and eluted proteins (eluate) were analyzed by immunoblotting using antibodies against the Strep epitope and GST. GST and GST fusion proteins are indicated by asterisks. (B) HrcL interacts with the conserved HrcU protein. GST, GST-HrcU, and GST-HrcU255-357 were immobilized on glutathione Sepharose and incubated with an E. coli lysate containing HrcL-c-Myc. TE and eluate were analyzed by immunoblotting using antibodies against the c-Myc epitope and GST. (C) HpaB interacts with HrcU. GST and GST-HrcU were immobilized on glutathione-Sepharose and incubated with an E. coli lysate containing HpaB-c-Myc. TE and eluate were analyzed as described for panel B. (D) Interaction studies with HpaB and HrcU255-357. GST and GST-HrcU255-357 were immobilized on glutathione-Sepharose and incubated with an E. coli lysate containing HpaB-c-Myc. TE and eluate were analyzed as described for panel B.