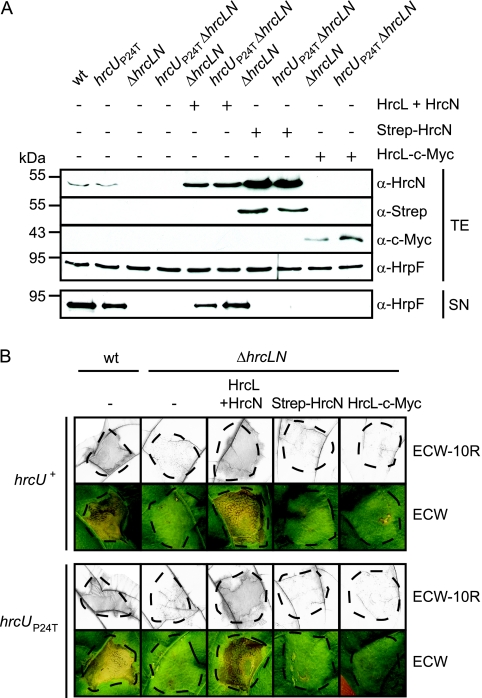
FIG. 9.
An hrcL hrcN double deletion mutant is impaired in in vitro T3S and bacterial pathogenicity. (A) In vitro T3S of the translocon protein HrpF is abolished in an hrcL hrcN double deletion mutant. Strains 85* (wild type [wt]), 85*hrcUP24T (hrcUP24T), 85*ΔhrcLN (ΔhrcLN), and 85*hrcUP24TΔhrcLN (hrcUP24TΔhrcLN) carrying the empty vector (−) or synthesizing Strep-HrcN, HrcL-c-Myc, or both HrcL and HrcN from construct pDhrcLN as indicated were incubated in secretion medium. Total protein extracts (TE) and culture supernatants (SN) were analyzed by immunoblotting using antibodies directed against HrcN, HrpF, the c-Myc, and the Strep epitope. (B) An hrcL hrcN double deletion mutant does not elicit phenotypic reactions in susceptible and resistant pepper plants. Strains 85* (wt) and 85*ΔhrcLN (ΔhrcLN) containing the hrcU wild-type (hrcU+) or the hrcUP24T (hrcUP24T) gene and carrying the empty vector (−) or Strep-hrcN, hrcL-c-myc, and hrcL hrcN expression constructs, as indicated, were inoculated into resistant ECW-10R and susceptible ECW pepper plants. For better visualization of the HR, leaves were bleached in ethanol 2 days after inoculation. Disease symptoms were photographed 7 days after inoculation. Dashed lines indicate the inoculated areas.