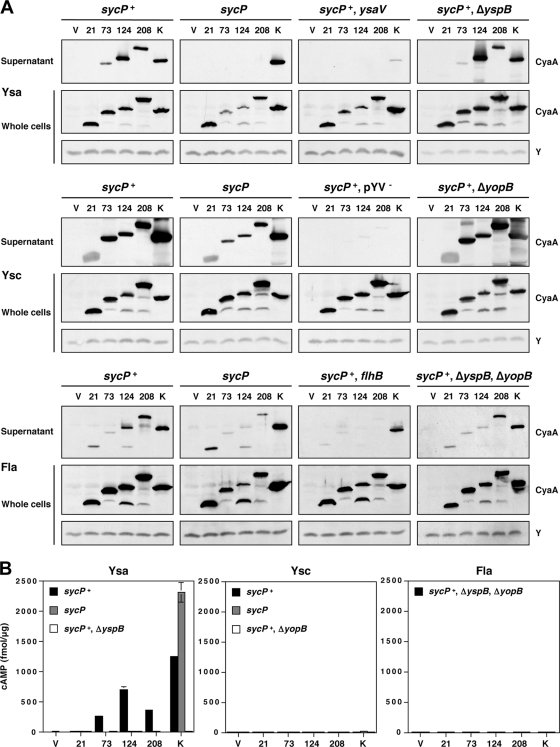
FIG. 3.
Secretion and translocation of proteins differing by the amino-terminal region of YspP fused to CyaA. (A) Secretion of various YspP-CyaA chimeras by the Ysa, Ysc, and flagellar T3S systems. Either pGY960 (sycP+) or pTM100 (sycP) was introduced in GY5774 (ΔyspB-sycB) and its derivative strains as listed: GY5831 (ysaV), GY6083 (ΔyspB), GY5829 (pYV−), GY6086 (ΔyopB), GY6128 (flhB), and GY6174 (ΔyspB ΔyopB). These strains also carried either the cloning vector pGY492 (V) or a derivative of this plasmid expressing a Ysp-CyaA chimera as listed: pGY967 (21), pGY968 (73), pGY969 (124), pGY709 (208), and pGY705 (K). The bacterial cells were grown in Ysa-, Ysc-, or flagellum (Fla)-inducing medium. The samples of supernatant (OD600 of 1) and whole-cell (OD600 of 0.1) fractions were then analyzed by Western blotting using an anti-CyaA antibody. Y was a cross-reactive protein that was detected by anti-CyaA antibody, working as a loading control. (B) Translocation of various YspP-CyaA chimeras by the Ysa, Ysc, and flagellar (Fla) T3S systems. HeLa cells were infected with selected strains of bacteria, as listed in panel A, expressing individual Ysp-CyaA chimeric proteins. Following the infections, the cytosolic level of cAMP for infected HeLa cells was measured as described in Materials and Methods. Results from a representative assay performed in duplicate are shown.