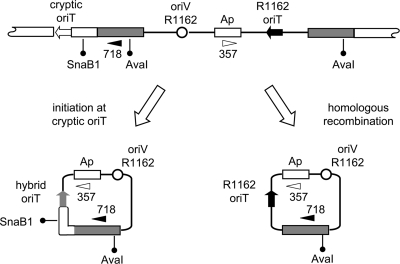
FIG. 5.
Alternate mechanisms for formation of ampicillin resistance plasmids in transconjugant cells. At the top is a map of the integrated plasmid pUT1951, and at the bottom are the structures of the plasmids that would be generated by initiation of transfer at the cryptic oriT (left) or by general homologous recombination within the duplicated Pectobacterium DNA (right). The sites for cleavage by AvaI and SnaBI, used to distinguish the two types of plasmids (Fig. 6A), are indicated. Also shown are the location of the primers (filled and closed horizontal arrowheads) for PCR analysis of excised plasmids in the donor (Fig. 6B).