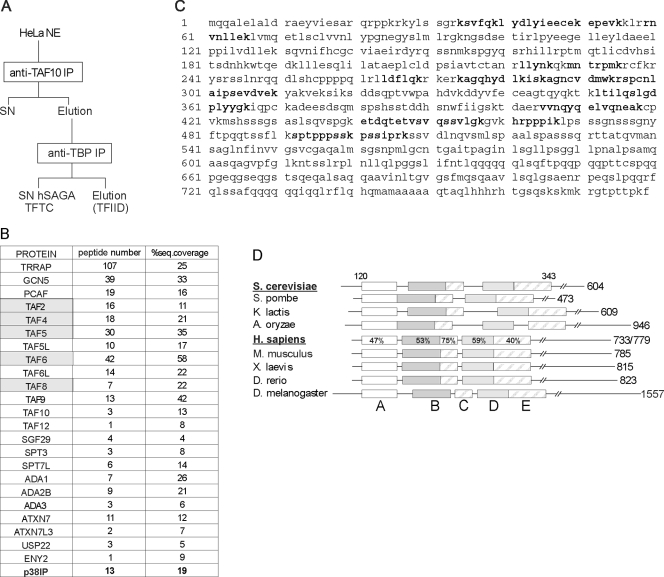
FIG. 1.
The newly identified hSAGA component shares sequence similarity with ySpt20. (A) Schematic representation of purifying TFTC (hSAGA) with a TAF10 IP followed by a TBP IP. hSAGA is in the final supernatant fraction (SN hSAGA). (B) Results of an MS analysis of the hSAGA/TFTC sample, purified as shown in panel A (for silver nitrate staining, see Fig. S1 in the supplemental material), are presented. The newly identified subunit, p38IP (called SPT20 further in this study) is bold; TAFs copurifying with the complex (see text) are marked with gray shading. (C) The complete amino acid sequence of the hSPT20 (p38IP) protein identified by MS in human hSAGA preparation is shown. Bold peptides were found in the MS sample. (D) Schematic representation of the multiple alignments highlighting the sequence homology between ySpt20 and the newly identified protein. The alignment covers amino acid positions 120 to 343 in the ySpt20 sequence, as marked on the top of the figure. Five evolutionarily conserved boxes were identified (represented with different shadings); the level of similarity between the yeast and human proteins is marked as a percentage. The length of each protein is marked on the right of the figure. For the human protein, we marked the two putative splice variants (see Fig. S3 in the supplemental material). S. cerevisiae, Saccharomyces cerevisiae; S. pombe, Schizosaccharomyces pombe; K. lactis, Kluyveromyces lactis; A. oryzae, Aspergillus oryzae; H. sapiens, Homo sapiens; M. musculus, Mus musculus; X. laevis, Xenopus laevis; D. rerio, Danio rerio; D. melanogaster, Drosophila melanogaster. A to E labeling of the boxes refers to Fig. S2 in the supplemental material, where the detailed sequence alignments of the boxes are shown. Note that the spacing between the conserved boxes is not conserved.