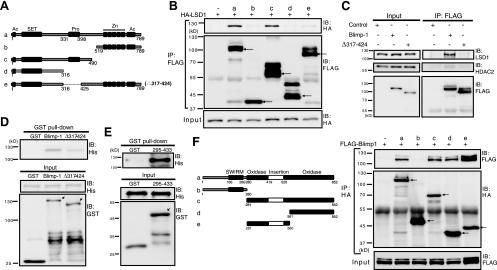
FIG. 4.
The Blimp-1 proline-rich domain is essential for interaction with LSD1. (A) Linear domain structure maps of full-length Blimp-1 (a) and various Blimp-1 deletion mutants (b to e). Known motifs: Ac, acidic domain; SET, PR domain resembling SET domain; Pro, proline-rich domain; Zn, five-zinc-finger motifs. (B) Blimp-1 or various mutated Blimp-1 expression constructs or empty vector (−) was cotransfected with expression vector HA-LSD1 into 293T cells for 2 days. Cell lysates were then harvested for immunoprecipitation (IP) and then immunoblot (IB) analysis. Arrows indicate Blimp-1 proteins. (C) Expression vectors encoding FLAG-tagged Blimp-1 or FLAG-tagged Δ317-424 or empty vector (Control) was transfected into 293T cells. Cells were harvested 2 days later, and the input and IP samples that were immunoprecipitated by anti-FLAG were analyzed by immunoblotting using the indicated antibodies. (D) Pull-down assay for GST-Blimp-1, GST-Δ317-424, or GST alone with His6-LSD1. (E) Pull-down assay for GST-295-433 or GST alone with His6-LSD1. Arrows indicate fusion proteins. (F) The oxidase domain containing the insertion tower domain in LSD1 is required for Blimp-1 interaction. Linear domain structures of LSD1 and its deletion mutants are illustrated at the left. Expression vectors encoding Blimp-1, LSD1, or various LSD1 mutants were cotransfected into 293T cells. Cell lysates were harvested after 2 days and subjected to co-IP. Arrows indicate LSD1 proteins. Molecular mass markers are indicated to the left of each blot.