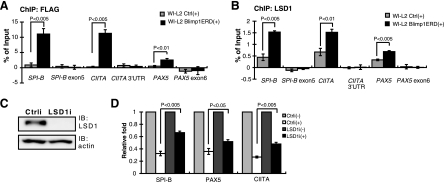
FIG. 6.
LSD1 binding to Blimp-1 target genes in vivo upon induction of Blimp-1. (A and B) Chromatin samples prepared from WI-L2 Blimp1ERD cells or WI-L2 ERD cells (WI-L2 Ctrl) induced by CdCl2 (5 μM) and 4-OHT (3 μM) for 10 h were immunoprecipitated with either anti-FLAG (A) or anti-LSD1 (B) for subsequent ChIP analysis. Regions encompassing or adjacent to Blimp-1 binding sites in the indicated gene loci were amplified by QPCR. A region located in each gene's 3′ untranslated region (UTR) or exonic region was amplified as a negative-control site. Input DNA amplified by QPCR was used to normalize data for the individual gene sites. Results are means ± standard errors of the mean from four independent experiments. (C) Immunoblot analysis showing the efficient knockdown of endogenous LSD1 in Blimp-1-ERD WI-L2 cells. (D) WI-L2 Blimp1ERD cells were either transduced with Ctrli or LSD1i for 5 days, and then CdCl2 and 4-OHT (+) were added or the cells were left untreated (−). After 48 h, cells were prepared for RT-QPCR analysis. Transcript levels of each indicated gene from untreated Ctrli or untreated LSD1i cells were set as 1 for normalization. Results are means ± standard deviations from three independent experiments.