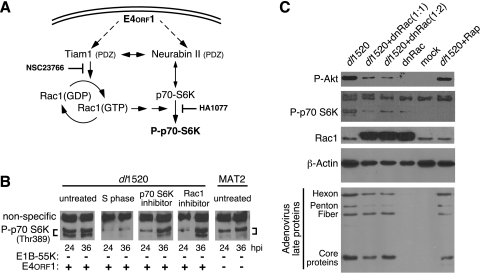
FIG. 5.
E4orf1-induced phosphorylation of p70 S6K and Akt may involve Rac1. (A) Schematic representation of a potential signaling pathway initiated by E4orf1 through the PDZ domain-containing proteins Tiam1 and neurabin II. Solid arrows identify known pathways and interactions. (B) HeLa cells were blocked at the G1/S border by exposure to HU for 24 h, released from the block, and infected 1 h later (S phase) or infected as an asynchronously dividing culture with the E1B-55K single-mutant virus dl1520 or the E1B-55K/E4orf1 double-mutant virus MAT2. At 4 hpi, the growth medium was replaced with fresh medium or with medium containing the p70 S6K inhibitor HA1077 at 50 mM or the Tiam1-Rac1 inhibitor NSC23766 at 40 μM. At 24 and 36 hpi, cellular proteins were analyzed by immunoblotting for phosphorylation of Thr389 on p70 S6K. A nonspecific cross-reacting protein is indicated which served as a loading control. The status of the relevant viral gene is indicated below each lane. (C) Asynchronously dividing HeLa cells were mock infected or infected with a nonreplicating adenovirus vector expressing dnRac1 (dnRac) at a multiplicity of 20 (1:1) or 40 (1:2). After 24 h, the cells were again mock infected or infected with the E1B-55K deletion mutant virus dl1520 at a multiplicity of 20. After 1 h, rapamycin (Rap) was added to 50 nM to one culture. Cells were harvested 36 h after infection with dl1520. Infected cell proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and analyzed by immunoblotting with monospecific antibodies (phospho-Akt, phospho-P70 S6K, Rac1, β-actin) or polyclonal serum specific for the adenovirus late proteins.