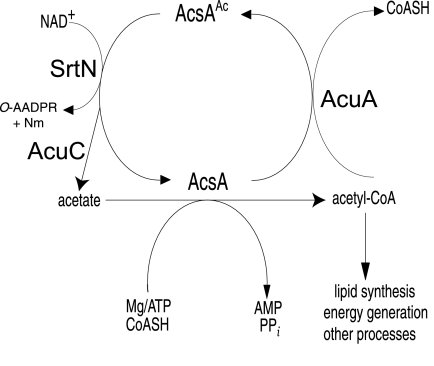
FIG. 4.
Schematic of the control of AcsA by the acetylation/deacetylation system of B. subtilis. While the data show that AcuA is the only acetyltransferase that can acetylate (deactivate) AcsA, the deacetylation (reactivation) step can be catalyzed by the SrtN or AcuC deacetylases. The physiological conditions under which each of the deacetylases is preferentially active are presently unknown. CoASH, free CoA.