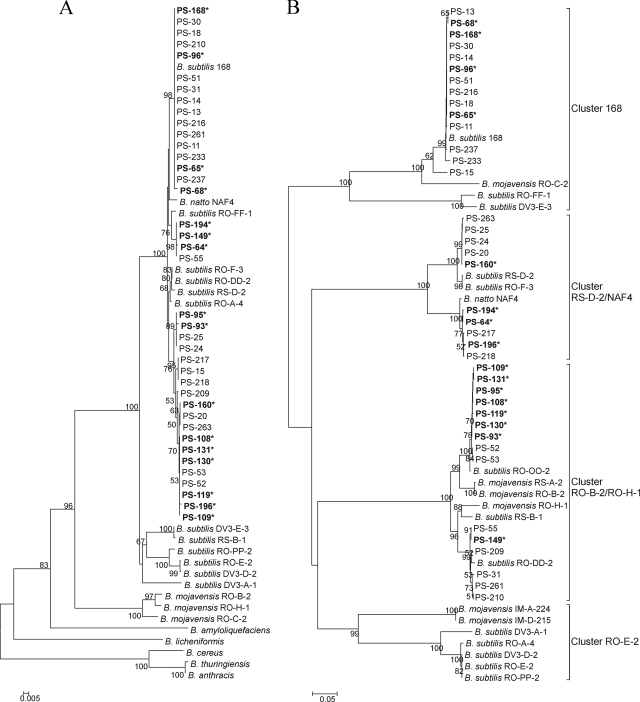
FIG. 1.
Minimum-evolution trees based on partial gyrA nucleotide sequences (610 bp) (A) and partial comQ sequences (701 bp) (B). Trees were drawn using the minimum-evolution method after multiple alignment in MEGA 4 software (50). The neighbor-joining algorithm was used to generate the initial tree. All positions containing gaps and missing data were eliminated from the data set. The numbers at internal branches represent the bootstrap values estimated from 1,150 resamplings. PS indicates newly acquired sequences of B. subtilis strains isolated from the riverbank soil, where sequences with and without asterisks originated from soil samples 2 and 1, respectively. In addition, gyrA and comQ sequences of desert B. subtilis strains (RO, RS, and DV) and other Bacillus strains obtained from the database were also included in the analyses. For clarity, clusters in panel B are named according to the B. subtilis tester strains used to identify their communication specificity in vivo (2). The top cluster in the similarity tree is referred as cluster 168, the second cluster as NAF4/RS-D-2, the third cluster as RO-H-1/RO-B-2, and the fourth cluster as RO-E-2.