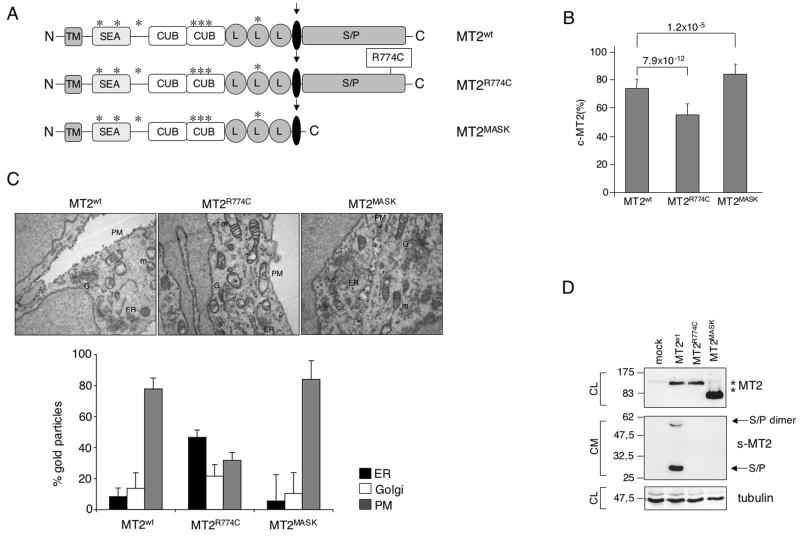
Figure 1. Matriptase-2 variants processing and plasma membrane localization.
(A) Schematic representation of matriptase-2 (MT2) functional domains and localization of the studied mutations [modified from (Ramsay et al., 2008)]. TM: transmembrane domain. SEA: sea urchin sperm protein, enteropeptidase agrin. CUB: complement protein subcomponents C1r/C1s, urchin embryonic growth factor and bone morphogenetic protein 1 domain. L: low density lipoprotein receptor class A domain. S/P: serine protease domain. The arrow indicates the cleavage activation site. Asterisks indicate the predicted consensus N-glycosylation sites. (B) Quantification of membrane bound matriptase-2 (m-MT2) by binding assay. Hela cells were transiently transfected with the wild type and mutant expressing vectors, or the empty vector, and analyzed for the amount of matriptase-2 on the cell surface. The amount was calculated as the ratio between the absorbance of unpermeabilized and permeabilized cells. Error bars indicate standard deviation. Statistical significance was calculated on a total of three experiments, made in triplicate. Exact P-values are shown above bars. (C) Electron microscopy and morphometric analysis of MT2wt, MT2R774C and MT2MASK. (D) Characterization of MT2. Whole cell extracts and concentrated media of transiently transfected HeLa cells were analyzed by 10% SDS-PAGE. Western blot was performed following standard procedures; MT2 was revealed by the anti-FLAG antibody. s-MT2: soluble MT2. S/P: serine protease domain. CL: cellular lysates; CM: conditioned medium. The equal loading was verified by α-tubulin.