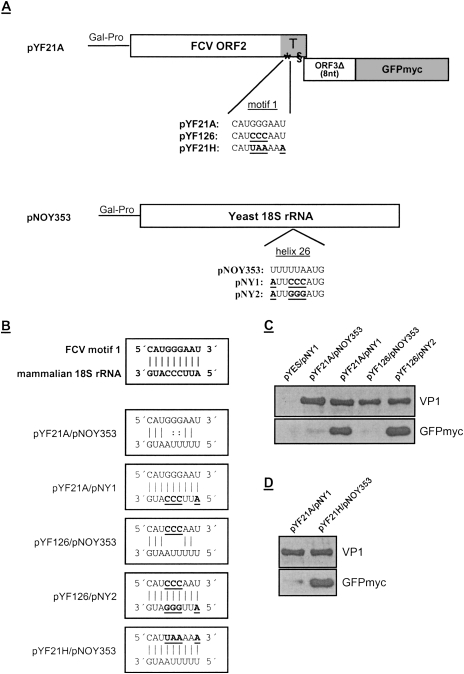
Figure 3.
Interaction of motif 1 of the FCV TURBS with helix 26 of 18S rRNA. (A) Schematic drawing of the plasmids introduced into the yeast strain NOY908. On top, pYF21A is indicated, containing two frames arranged the same way as in FCV subgenomic mRNA. The first frame corresponds to FCV ORF2, codes for VP1, and contains the TURBS (T, highlighted in gray) with the two essential motifs indicated. The second frame starts with the first 8 nt of the VP2 coding sequence that is fused with the sequence coding for GFP with a 3′-terminal c-Myc tag (GFPmyc). Below the schematic representation of pYF21A, the motif 1 sequence is shown for FCV wild type and for substitution mutants pYF21H and pYF126, with the exchanges within motif 1 highlighted. Below, the pNOY353 construct is shown, coding for the 18S rRNA of yeast, and the sequence of helix 26 (nucleotides 1056–1164 in yeast 18S rRNA) is given. Mutations introduced into this region in the constructs pNY1 and pNY2 are indicated. (B) On top, the putative base pairing between the FCV TURBS motif 1 and the mammalian 18S rRNA sequence is indicated by vertical lines. Below, the possible hybridizing residues of the motif 1 regions of the indicated pYF constructs and the helix 26 sequences of the 18S rRNA constructs are illustrated for the plasmid combinations introduced into the yeast strain NOY908. (C,D) The proteins translated in the yeast cells, transfected with the plasmid combinations given above the gels, are shown in a Western blot analysis with antisera against VP1 (top panel) or GFP (bottom panel). Please note that in comparison with C the blot with the anti GFP serum in D was exposed for a much shorter time to be able to demonstrate the increase in GFPmyc expression in the right lane. The ratio between VP1 and GFPmyc for the construct combination pYF21A/pNY1 can therefore not be compared between the blots C and D. (Gal-Pro) Yeast galactose-promoter.