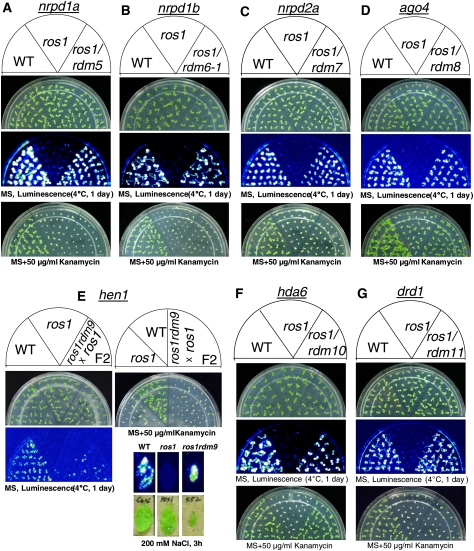
Figure 1.
Luminescence and kanamycin resistance phenotypes of ros1 suppressor mutations in known RdDM components. Wild type, ros1, and the double mutants ros1rdm5 (A), ros1rdm6-1 (B), ros1rdm7 (C), ros1rdm8 (D), ros1rdm9 (E), ros1rdm10 (F), and ros1rdm11 (G) were either grown on MS plates for 7–10 d and luminescence was imaged after cold treatment (1 d, 4°C), or were grown on MS plates supplemented with 50 μg/mL kanamycin and the pictures were taken after 1–2 wk. Because the ros1rdm9 mutant is sterile, the F2 progenies from a cross between ros1rdm9 and ros1, instead of ros1rdm9, were grown on plates for phenotype assay. The luminescence of ros1rdm9 was also assayed using NaCl-treated leaves from soil-grown plants. Because the rdm5, rdm6, rdm7, rdm8, rdm9, rdm10, and rdm11 mutants were identified as nrpd1a, nrpd1b, nrpd2a, ago4, hen1, hda6, and drd1, respectively, the names of these mutants are labeled on the top of each panel.