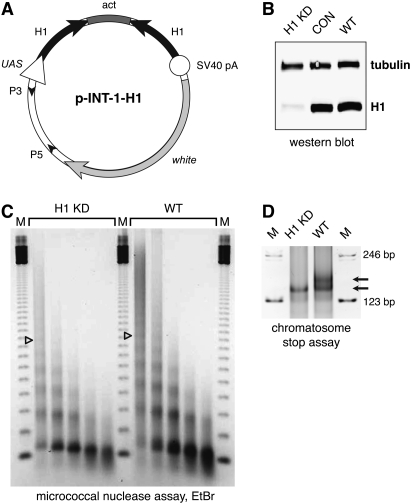
Figure 1.
Depletion of histone H1 in Drosophila. (A) Transgenic RNAi construct for sequence-specific post-transcriptional silencing of the Drosophila linker histone H1 gene. Two identical fragments of the H1 coding sequence (the first 600 bp) were inserted in opposite orientations on both sides of the first intron of the actin 5C gene in the pINT-1 vector. The expression of H1-specific dsRNA is driven by the GAL4-responsive UAS promoter. (Open triangle) UAS promoter; (black arrows) H1 cDNA fragments; (dark-gray box) act5C intron; (open circle) SV40 polyadenylation site; (light arrow) white gene; (small black arrowheads) P-element sequences. (B) The expression of H1 protein in the third instar (L3) larval salivary glands is abrogated by RNAi. H1 synthesis was inhibited by H1-specific dsRNA transcribed from p-INT-1-H15M transgene driven by the GAL4 transactivator encoded by the Tubulin-GAL4 transgene at 29°C (from the beginning of embryonic development to L3). H1 protein levels in salivary gland lysates of H1-depleted animals (H1 KD) were compared with those in salivary glands of the wild-type (WT) and pINT-1-Nautilus (CON) animals by immunoblotting using an antiserum against Drosophila histone H1. Protein loading was controlled by immunoblotting for tubulin. (C) Nucleosome repeat length (NRL) is reduced in L3 larval chromatin upon depletion of H1 by RNAi. H1 synthesis was inhibited by H1-specific dsRNA as described in B. Nuclei from L3 larvae were subjected to partial micrococcal nuclease digestion, and the DNA was analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis and EtBr staining. The NRL in knockdown animals (H1 KD) was calculated to be ∼176 bp compared with ∼188 bp in the wild-type control (WT). Open triangles indicate the positions of the hexanucleosome bands in each sample. (M) 123-bp DNA ladder. (D) Chromatosome particles are depleted in the chromatin of H1 knockdown larvae. Chromatin from H1 knockdown (H1 KD) and wild-type (WT) larvae was prepared and digested extensively with MNase as in C. The DNA was analyzed by native PAGE and EtBr staining. In H1 knockdown larvae, the chromatosome band (top arrow) is substantially depleted in comparison with the wild-type control larvae. (Bottom arrow) Core particle; (M) 123-bp DNA ladder.