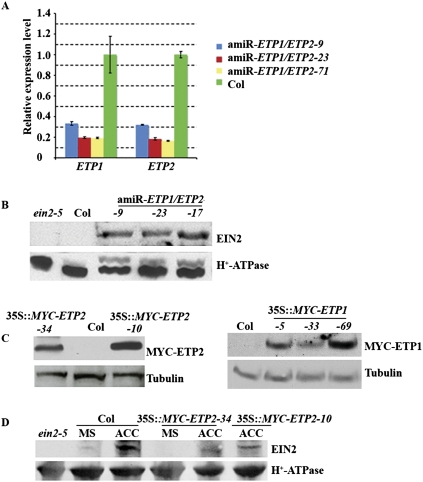
Figure 3.
ETP1 and ETP2 are regulators of EIN2 levels. (A) qPCR analysis of ETP1 and ETP2 transcript levels in amiR-ETP1/ETP2 mutant plants. Total RNA was extracted from the leaves of 3-wk-old light-grown plants. The data were normalized to the corresponding actin (input) controls. The data shown are the means ± SD of three independent experiments. (B) EIN2 protein accumulates in amiR-ETP1/ETP2 mutant plants. (C) MYC-ETP1 or ETP2 accumulates in 35S∷MYC-ETP1 or MYC-ETP2 transgenic plants, respectively. Wild-type Col-0 Arabidopsis plants were transformed with a binary vector carrying the MYC tag that fused with ETP1 or ETP2 open reading frame. Total proteins from 35S∷MYC-ETP1 or MYC-ETP2 transgenic plants were subjected to immunoblotting with anti-MYC antibody. The same membranes were stripped and subjected to immunoblotting with an anti-tubulin antibody as loading control. (D) Overexpression of ETP2 causes reduction of EIN2 protein. Wild-type Col-0 and ETP2 overexpression plants grown on soil for 3 wk and the total protein lysates from leaves were subjected to immunoblotting with EIN2 antiserum. The same membrane was stripped and subjected to immunoblotting with an anti-H+-ATPase antibody as a lane loading control.