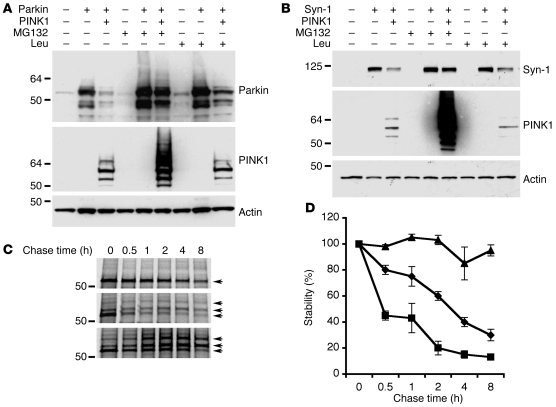
Figure 3. PINK1 promotes proteasomal degradation of Parkin and Synphilin-1.
(A and B) SH-SY5Y cells coexpressing PINK1-flag and Parkin-VSVG (A) or PINK1-flag and Synphilin-1–EGFP (Syn-1; B) were treated with either MG132 or leupeptin (Leu). Steady-state levels of Parkin, Synphilin-1, PINK1, and actin (loading control) are shown. (C and D) Expression of PINK1 reduced Parkin stability via the proteasomal pathway. Cells transfected with Parkin alone (C; top panel), Parkin and PINK1 (C; middle panel), or Parkin and PINK1 with MG132 treatment (C; bottom panel) were pulse-labeled, followed by chasing for the indicated time intervals. Levels of Parkin were detected by immunoprecipitation. Results from a representative experiment (C) and quantitation of 3 independent experiments are shown (D). Multiple Parkin bands likely representing ubiquitinated Parkin were detected in the presence of PINK1 (arrows). (D) Diamonds indicate Parkin alone, squares indicate Parkin and PINK1, and triangles indicate Parkin and PINK1 with MG132 treatment.