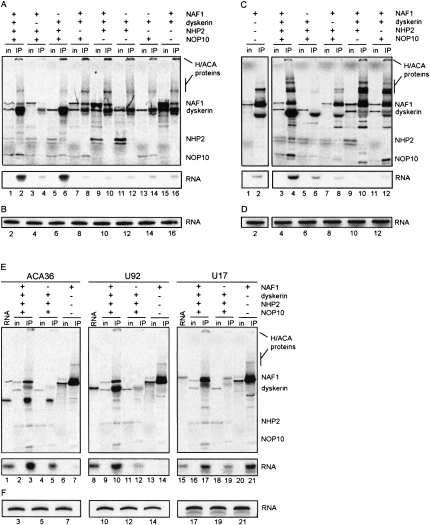
FIGURE 3.
Binding of NAF1 to hTR204 requires the trimer dyskerin/NOP10/NHP2. (A,C) RRL mixtures containing 35S-labeled proteins and 32P-labeled hTR204 were subjected to (A) dyskerin IP or (C) NAF1 IP and analyzed by (top) PAGE. The presence or absence of each protein in the RRL mixtures is indicated by (+) or (−), respectively. Input lanes (in) did not contain the 32P-labeled hTR204. (C, left,right) Come from the same gel exposition. (Bottom) Only the 32P signal of the protein gel (see legend to Figure 2B for details). (B,D) Labeled hTR204 recovered from supernatants of dyskerin or NAF1 IPs (see A and C, respectively) was analyzed on 8% denaturing polyacrylamide gels. Lanes are numbered in accordance with the corresponding dyskerin and NAF1 IPs shown in (A) and (C), respectively. (E) RRL mixtures containing 35S-labeled proteins and 32P-labeled ACA36, U92, or U17 were subjected to NAF1 IP and analyzed by (top) PAGE. The presence or absence of each protein in the RRL mixtures is indicated by (+) or (−), respectively. Input lanes (in) did not contain the radiolabeled RNAs. Labeled ACA36 (lane 1), U92 (lane 8), and U17 (lane 15) RNAs not incubated in RRL are shown. (Bottom) Only the 32P signal of the protein gels presented in top panels. (F) Labeled ACA36, U92, or U17 recovered from supernatants of NAF1 IPs shown in (E) were analyzed on 8% denaturing polyacrylamide gels. Lanes are numbered in accordance with the corresponding IPs shown in (E).