Fig. 10.2.
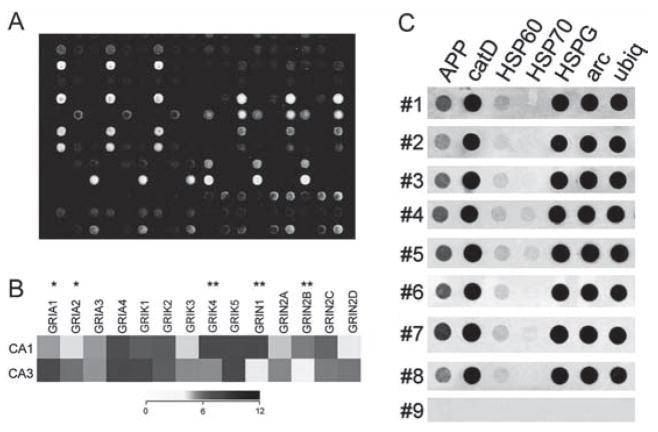
Representative array platforms illustrating utility of RNA amplification procedures for single cell and population cell analysis. (A) Spotted cDNA array platform using RNA amplified from individual hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons from normal control brains and from neurofibrillary tangle (NFT) bearing CA1 neurons from Alzheimer’s disease (AD) patients.
(B) Dendrogram demonstrating relative expression levels of representative genes in CA1 and CA3 pyramidal neurons microaspirated from human hippocampus. A heatmap matrix plot illustrates relative expression levels for individual glutamate receptor transcripts in CA1 and CA3 neurons. A single asterisk indicates a significant increase in expression in CA3 neurons as compared to CA1 neurons and a double asterisk denotes a significant increase in expression in CA1 neurons as compared to CA3 neurons. Key: GRIA 1, alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxa-zolepropionate receptor 1 (AMPA1); GRIA2, AMPA2, GRIA3, AMPA3, GRIA4, AMPA4; GRIK1, kainate (KA) receptor GluR5; GRIK2, KA GluR6; GRIK3, KA GluR7; GRIK4, KA receptor KA1; GRIK5, KA receptor KA2; GRIN1, N-methyl D-aspartate receptor 1 (NR1); GRIN2A, NR2A; GRIN2B, NR2B; GRIN2C, NR2C; GRIN2D, NR2D. Adapted from Ginsberg and Che 2005 [32].
(C) Single-cell array analysis of human CA1 pyramidal neurons using custom-designed cDNA arrays and TC RNA amplification. Representative arrays illustrate a wide dynamic range of hybridization signal intensities for eight human postmortem cases (numbers 1–8). The negative control (number 9) is a single CA1 pyramidal neuron from the first case (number 1) that does not have the primers necessary for TC RNA amplification. In addition, a moderate variation of gene level expression across the eight human cases is observed, indicating the utility of using postmortem human samples for normative and neuropathological investigations. Key: APP, amyloid-β precursor protein; catD, cathepsin D; HSP60, heat shock protein 60; HSP70, heat shock protein 70; arc, activity regulated cytoskeletal-associated protein; ubiq, ubiquitin thiolesterase. Adapted from Ginsberg and Che 2002 [10]