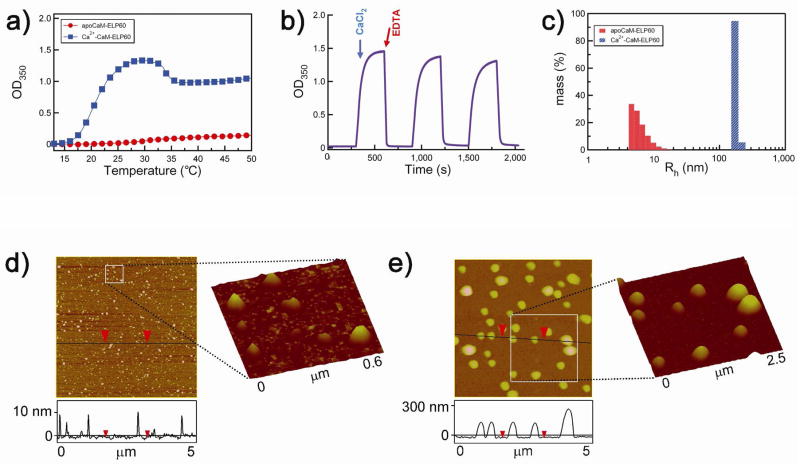
Figure 3.
Effect of sequential addition of Ca2+ and EDTA on LCST behavior of CaM-ELP60. a) Turbidity at 350 nm (OD350) as a function of solution temperature for apoCaM-ELP60 (filled circles, red), Ca2+-CaM-ELP60 (filled squares, blue). b) Reversible control of self-assembly of CaM-ELP fusion as a function of Ca2+ binding. The OD350 was measured as a function of time after sequential injection of Ca2+ followed by EDTA as indicated by the arrows. Three cycles of addition of Ca2+ followed by EDTA are shown in the Figure. c) Rh measured by DLS of apoCaM-ELP60 and Ca2+-CaM-60, showing the existence of apoCaM-ELP60 as a soluble monomer and Ca2+-CaM-ELP60 as a monodisperse nanoparticle with a Rh of ~180 nm. Tapping mode AFM images of: d) apoCaM-ELP60 and e) Ca2+-CaM-ELP60. Vertical scale bar indicates height of the features in the 5×5 μm images. The squares demarcate regions of d, and e, whose magnified views are shown as 3-D reconstructions of the AFM images.