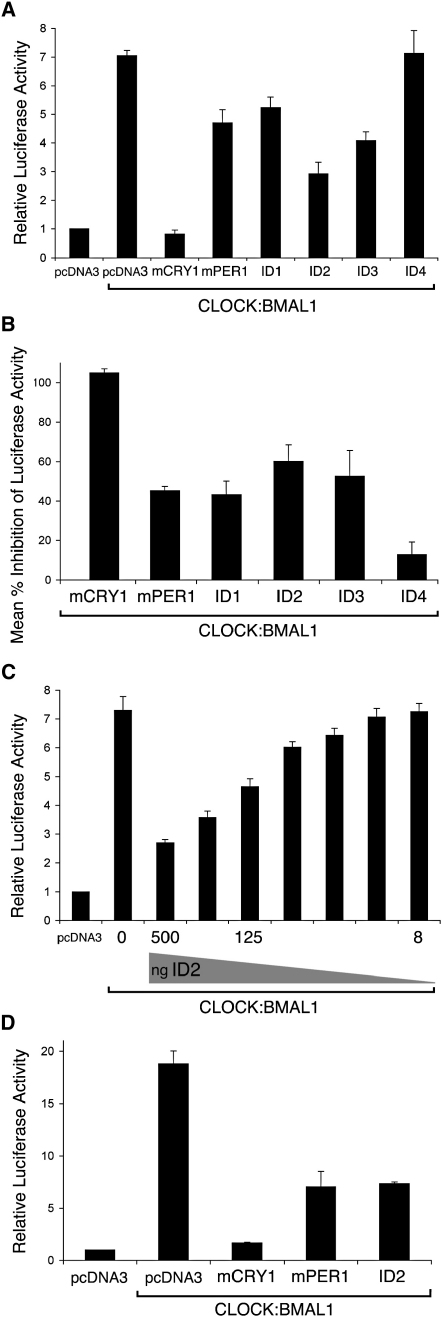
Figure 4.
ID Proteins Can Potently Inhibit CLOCK:BMAL1 Transactivation of the mPer1 and AVP Promoters
(A) Effect of cotransfection of CLOCK and BMAL1 with ID constructs on transactivation of the mPer1-promoter. Data are mean ± SEM (n = 3–6) relative luciferase activity. All groups except pcDNA3.1 (empty vector) were transfected with equal amounts of CLOCK and BMAL1 expression vectors. As expected, luciferase activity was increased by the presence of plasmids encoding CLOCK and BMAL1, but not by either CLOCK or BMAL1 alone. Level of inhibition by clock proteins mCRY1 and mPER1 was similar to published reports [18, 37].
(B) Summary of five independent experiments showing consistent inhibition of CLOCK:BMAL1 transactivation at the E-box of the mPer1-promoter by ID1 (43%), ID2 (60%), and ID3 (53%) at levels similar or greater than shown by the clock protein mPER1. ID4 showed limited inhibitory activity. Values are mean ± SEM percentage inhibition of luciferase activity.
(C) Dose-dependent repression of CLOCK:BMAL1 activity by ID2. Serial dilution of ID2 expression plasmid cotransfected with CLOCK and BMAL1 plasmids is shown.
(D) Effect of cotransfection of CLOCK and BMAL1 with an ID2 expression plasmid on transactivation of the arginine vasopressin (AVP)-promoter. Data are mean ± SEM (n = 3) relative luciferase activity from one representative experiment. The amount of inhibition by ID2 is similar to that of mPER1. Level of inhibition by mPER1 was similar to published reports [18, 37].