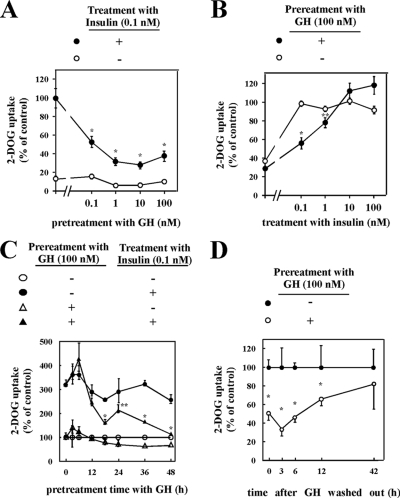
FIGURE 1.
Effects of chronic GH pretreatment on insulin-induced glucose uptake. A, 3T3-L1 adipocytes were serum-starved for 2 h, pretreated with the indicated concentrations of GH for 24 h, and then stimulated without (○) or with (•) 0.1 nm insulin for 15 min. Cells were assayed for glucose uptake as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Glucose uptake by cells without GH pretreatment and with insulin stimulation was used as control. B, 3T3-L1 adipocytes were serum-starved for 2 h, pretreated without (○) or with (•) 100 nm GH for 24 h, and then treated with the indicated concentrations of insulin for 15 min. Cells were assayed for glucose uptake as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Glucose uptake by cells without GH pretreatment and with 0.1 nm insulin stimulation was used as control. C, 3T3-L1 adipocytes were pretreated without (•, ○) or with (▴, ▵) 100 nm GH for indicated periods, and then treated without (○, ▵) or with (•, ▴) 0.1 nm insulin for 15 min. Next, cells were assayed for glucose uptake as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Glucose uptake by cells without GH treatment and without insulin stimulation was used as control. The results are presented as the means ± S.E. of five wells. The difference between insulin-stimulated cells with and without GH pretreatment is significant with p < 0.01 (*) or p < 0.05 (**). D, cells were pretreated with 100 nm GH for 24 h, and GH was washed out by changing medium without GH, followed by incubation for the indicated time. Cells were treated with 0.1 nm insulin for 15 min, and glucose uptake was measured. Glucose uptake by cells without GH pretreatment was used as control. The results are presented as the means ± S.E. of five wells. The difference between cells with and without insulin stimulation is significant with p < 0.05 (*). 2-DOG, 2-deoxy-d-glucose.