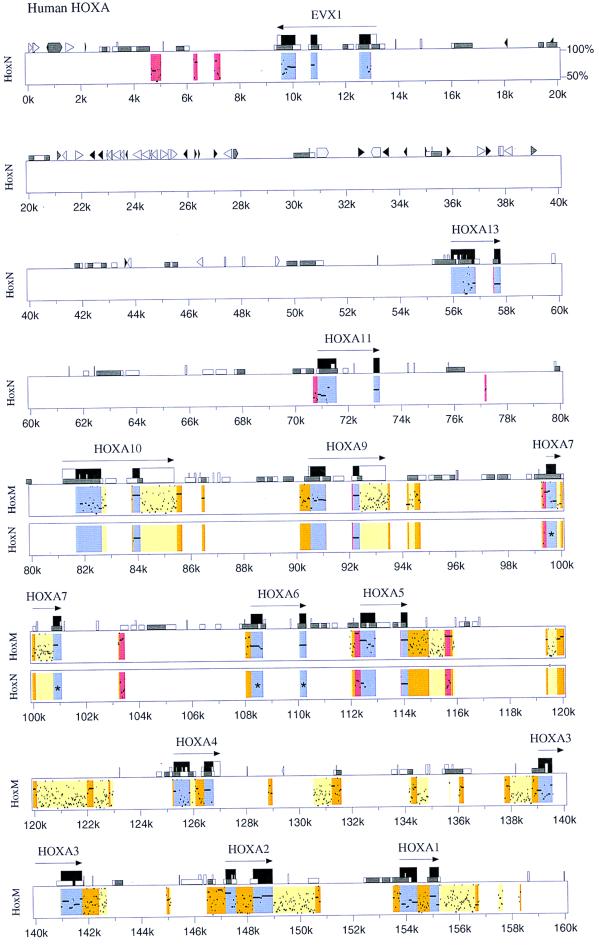
Figure 3.
Comparisons of nucleotide sequence between human HoxA, Heterodontus HoxM, and HoxN Hox clusters. Sequence comparisons are based on the human HoxA cluster as a reference. Kilobase (k) markings relate to the human HoxA cluster. Actual spacings between genes and gene dropouts are shown in Fig. 1. Color codes and symbols are as follows. Blue signifies coding regions. Yellow indicates weakly conserved noncoding regions. Orange indicates strongly conserved noncoding regions. Red indicates noncoding sequences conserved in both Heterodontus HoxM and HoxN clusters at the same position. The long horizontal arrows indicate direction of transcription. Tall black boxes indicate protein coding regions. Tall open boxes show, where possible, untranslated regions of a gene as determined from mRNA sequences in GenBank (namely, Evx-1, HoxA10, HoxA9, and HoxA4). Medium size open boxes (e.g., at position 13.9k) denote simple repeats and low-complexity regions. Short open boxes (e.g., 4k) demarcate CpG islands, with open boxes indicating a CpG/GpC ratio between 0.6 and 0.75 and gray indicating a ratio above 0.75. Interspersed repeat elements are shown as triangles and pointed boxes, where black triangles signify MIR elements, light gray triangles represent SINES other than MIR, light gray pointed boxes designate LINE1, and dark gray represent all other repetitive elements. Asterisks (*) in the middle of exons of Hox6 and Hox7 genes of HoxN indicate gene dropouts of those Hox genes in HoxN cluster.