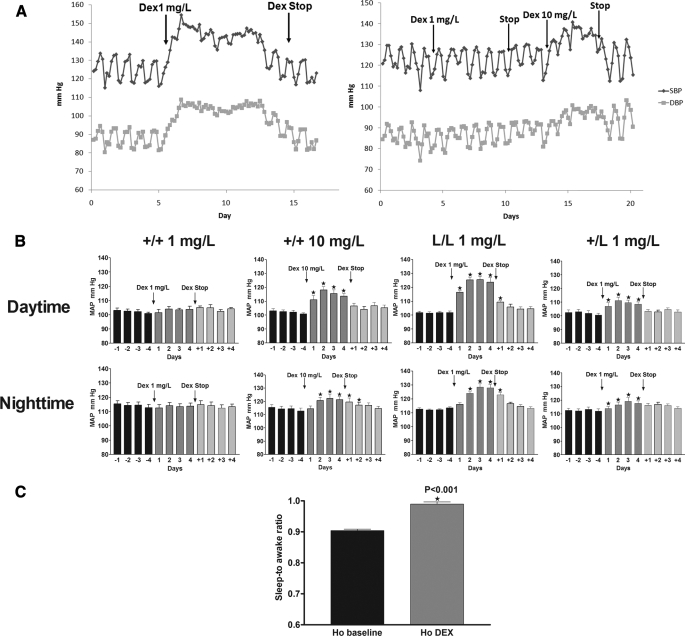
FIGURE 4.
The GRM610L allele increases sensitivity to exogenous glucocorticoids in vivo. A, baseline blood pressure was recorded for 4 days in an L/L mouse (left panel) or in a +/+ (right panel) littermate. Subsequently, dexamethasone was provided in the drinking water (1 mg/liter) and blood pressure was followed radiotelemetrically. The blood pressure tracing of a representative mouse is shown. The initiation and termination of dexamethasone are indicated. Each data point represents the average of all measurements obtained within a 4-h window. DEX (1 mg/liter) induces a rapid rise in BP with loss of normal diurnal variation in L/L mice, but not in +/+ littermates; and that this rise in BP rapidly reverses following discontinuation of dexamethasone. Subsequently, 10 mg/liter DEX was provided to the +/+ mouse, and a rapid rise in BP was observed. B, 12-h means of MAP in male GR +/+ (n = 6), L/L (n = 6), or +/L (n = 6) littermates before (baseline) and after treatment with DEX (1–10 mg/liter) in the drinking water. MAP values were measured by telemetry. Values were analyzed as 12 h means reflecting the day and night periods and expressed as mean ± S.E.; C, mean ± S.E. values for sleep-to awake BP ratio of GR L/L mice before and after 1 mg/liter DEX treatment.