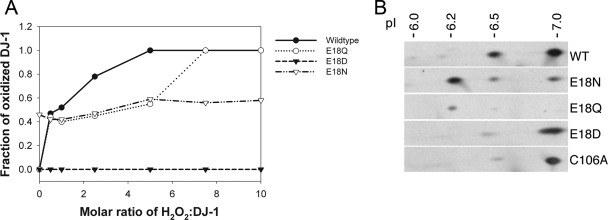
FIGURE 2.
Substitutions at position 18 of DJ-1 impact
Cys106-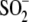 formation. A, oxidation of Cys106 in vitro
to Cys106-
formation. A, oxidation of Cys106 in vitro
to Cys106-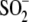 . Mass
spectrometry was used to monitor the oxidation of DJ-1 as a function of
hydrogen peroxide concentration in solution. The fraction of protein oxidized
was calculated as a ratio of the integrated area of the oxidized protein peak
to the total area of both the oxidized and reduced peaks. A comparison of the
oxidation curves of these proteins shows that every substitution at position
18 results in diminished oxidation compared with the wild-type protein,
although the extent of this diminution varies among the three substitutions.
E18D abolishes the ability of Cys106 to be oxidized to
cysteine-sulfinic acid, and E18N oxidizes very easily at low
H2O2 levels. B, oxidation of DJ-1 in
vivo. Human M17 neuroblastoma cells were transfected with V5-tagged
versions of the indicated DJ-1 constructs (wild type (WT), E18N, E18Q, E18D,
and C106A, from top to bottom) and exposed to 300
μm paraquat for 24 h. Protein extracts were separated on
two-dimensional gels and blotted for DJ-1. Estimated pI values for each
isoform are indicated above the blots. Images are
representative of duplicate experiments for each construct.
. Mass
spectrometry was used to monitor the oxidation of DJ-1 as a function of
hydrogen peroxide concentration in solution. The fraction of protein oxidized
was calculated as a ratio of the integrated area of the oxidized protein peak
to the total area of both the oxidized and reduced peaks. A comparison of the
oxidation curves of these proteins shows that every substitution at position
18 results in diminished oxidation compared with the wild-type protein,
although the extent of this diminution varies among the three substitutions.
E18D abolishes the ability of Cys106 to be oxidized to
cysteine-sulfinic acid, and E18N oxidizes very easily at low
H2O2 levels. B, oxidation of DJ-1 in
vivo. Human M17 neuroblastoma cells were transfected with V5-tagged
versions of the indicated DJ-1 constructs (wild type (WT), E18N, E18Q, E18D,
and C106A, from top to bottom) and exposed to 300
μm paraquat for 24 h. Protein extracts were separated on
two-dimensional gels and blotted for DJ-1. Estimated pI values for each
isoform are indicated above the blots. Images are
representative of duplicate experiments for each construct.