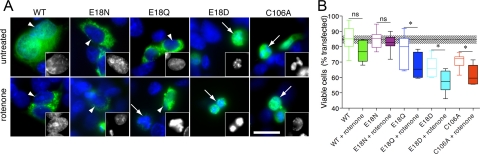
FIGURE 5.
DJ-1 Glu18 substitutions affect cellular resistance to rotenone-induced toxicity. A, nuclear morphology as a marker of rotenone-induced loss of cell viability. M17 neuroblastoma cells were transiently transfected with V5-tagged WT, E18N, E18Q, E18D, or C106A DJ-1 constructs, as indicated, and either left untreated (upper panels) or exposed to 200 nm rotenone for 24 h (lower panels). Cells were stained for V5 (green) and counterstained with Hoechst 33342 (blue) and scored as having intact nuclei (arrowheads) or fragmented/shrunken nuclei (arrows). The insets show examples of nuclei from the blue channel at higher magnification. The scale bar in the bottom right panel represents 20 μm and applies to all images. B, cells were transfected as in A with WT (green), E18N (magenta), E18Q (blue), E18D (cyan), and C106A (red) DJ-1 variants. Cell viability is expressed as the percentage of transfected (V5-positive) cells that had intact nuclei compared with all transfected cells. Each box plot represents data from three randomly selected microscope fields (between 26 and 75 cells/field) counted in each of three independent experiments for an overall n = 9 per construct. Horizontal lines, median values; boxes, upper and lower quartiles; range bars, the range of percentage viabilities for all fields counted. The dotted line represents mean viability counted in untransfected cells from the same cultures, with the shaded box indicating one S.D. value (84.6 ± 2.7% viability, n = 9 fields, mean of 28 cells/field). Differences were analyzed comparing the indicated untreated and rotenone-treated cells for the same construct; *, p < 0.05 by one-way ANOVA (p < 0.001 overall) with Newman-Kuell's post hoc tests. ns, not significant.