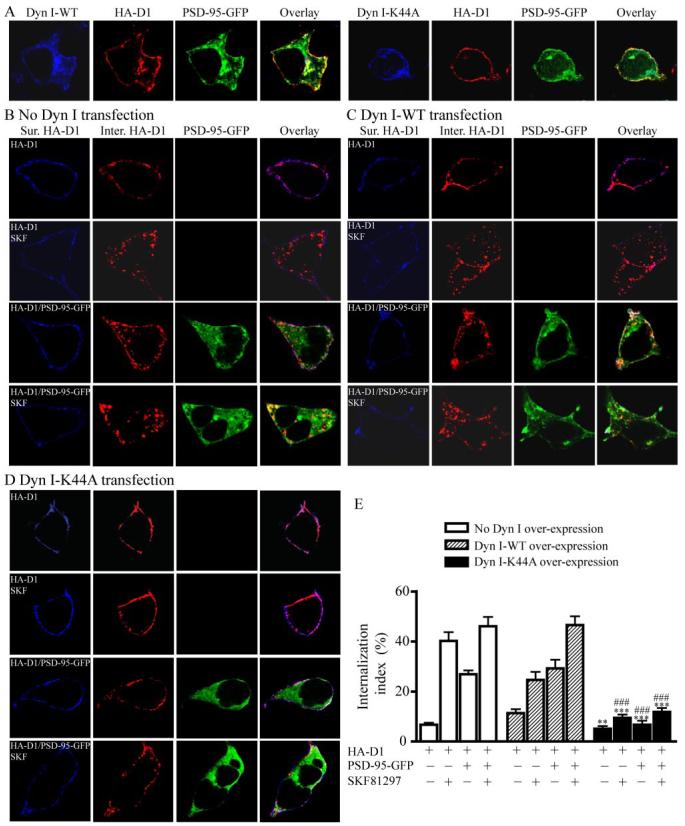
FIGURE 7. PSD-95-mediated constitutive D1 internalization is dynamin-dependent.
A, representative images showing that overexpression of Dyn I-K44A, but not Dyn I-WT, abolished the intracellular D1 localization in HEK293 cells co-expressing HA-D1 and PSD-95-GFP. B, constitutive and SKF81297-stimulated D1 internalization in HEK293 cells expressing HA-D1 or HA-D1/PSD-95-GFP. Sur., surface; Inter., internalized. C, overall lack of effect of Dyn I-WT overexpression on the constitutive and stimulated D1 internalization in HEK293 cells. D, Dyn I-K44A overexpression abolished the constitutive and stimulated D1 internalization in HEK293 cells. E, summary of K44A effect on D1 internalization from (B–D). HEK293 cells were transfected with combinations of cDNAs encoding HA-D1, PSD-95-GFP, Dyn I-WT, or Dyn I-K44A. Receptor internalization shown in B–E was performed and quantified as in Fig. 5. Data were presented as mean ± S.E. (n = 15– 41 cells for each group). **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.0001 versus corresponding Dyn I-WT transfection controls; ###, p < 0.0001 versus corresponding no Dyn I transfection controls, Student’s t tests.