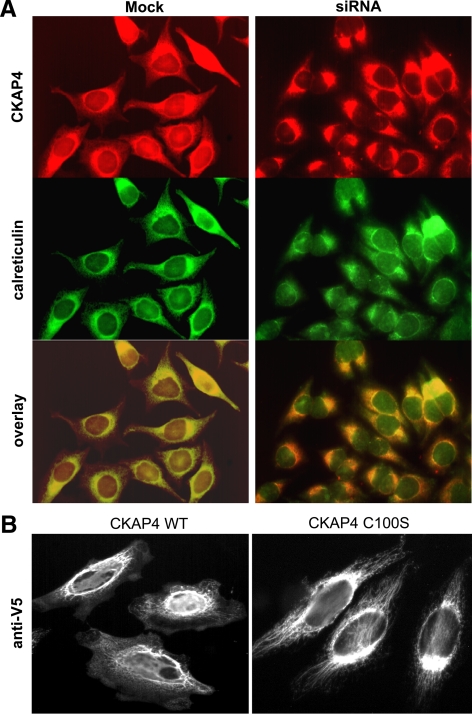
Figure 3.
DHHC2-mediated palmitoylation of CKAP4 on cysteine 100 regulates its trafficking from the ER to the PM. (A) Mock-transfected or DHHC2 siRNA-transfected HeLa cells were grown on multiwell glass slides, fixed, and incubated with a mAb G1/296 against CKAP4 (anti-CLIMP-63, diluted 1:100) followed by a TRITC-labeled, goat anti-mouse secondary antibody (diluted 1:1000) or with a pAb against calreticulin (diluted 1:1000) followed by a FITC-labeled, goat anti-rabbit secondary antibody (diluted 1:1000). Controls included cells processed without primary and/or secondary antibodies. Images were acquired using a Nikon TE2000 epifluorescence microscope with NIS Elements software and overlayed using Adobe Photoshop software (San Jose, CA). In HeLa cells with reduced DHHC2 expression, CKAP4 localization is restricted to the ER. (B) HeLa cell lines stably expressing CKAP4 WT-V5 or the palmitoylation-incompetent mutant, CKAP4 C100S-V5, were grown on multiwell glass slides, fixed, and immunolabeled with a FITC-conjugated mAb antibody against the V5 epitope (1:500). CKAP4 WT was expressed on the plasma membrane and perinuclear membranes, whereas CKAP4 C100S expression was restricted to the ER. Epifluorescence images in B were made with a 100× 1.45 NA oil immersion objective.