Figure 3.
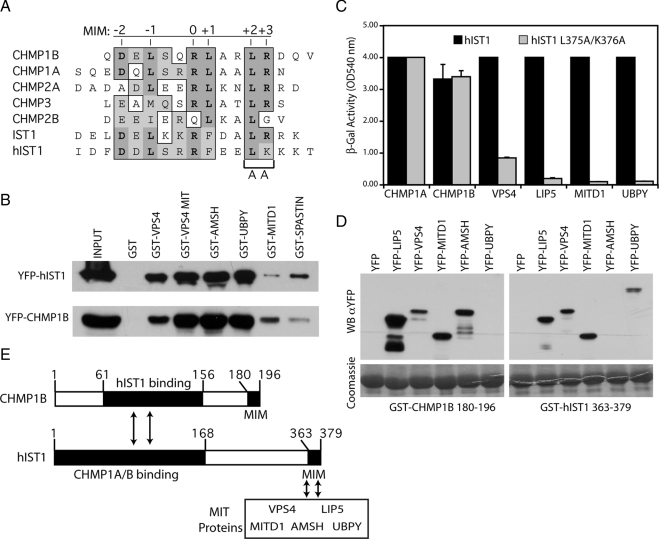
IST1 contains a functional MIM. (A) Sequence alignment of the MIMs from the indicated human ESCRT-III proteins and the human and yeast IST1 genes. Positions of the six MIM residues contacting Vps4 MIT domain are indicated on top of the alignment and conserved amino acids are shaded in gray. (B) Coprecipitation assays showing binding of the indicated MIT containing proteins to YFP-CHMP1B or YFP-hIST1. One percent of the starting cell lysate (INPUT) and 10% of the volume eluted from the beads were analyzed by Western blot with α-GFP antibody. (C) hIST1 residues in MIM's position +2 and +3 were mutated (hIST1 L375A/K376A), and interactions with ESCRT-III and MIT-containing proteins were monitored using yeast two-hybrid assays. Error bars indicate the SD from the mean of triplicate measurements. (D) Cell lysates from bacteria expressing CHMP1B's MIM (GST-CHMP1B 180-196) or hIST1's MIM (GST-hIST1 363-379) were tested by coprecipitation assays for binding to the indicated MIT-containing proteins fused to YFP and binding was monitored with α-GFP mAb (WBαYFP). Bottom, GST fusion protein expression in cell lysates with Coomassie staining. (E) Schematic representation of CHMP1B and hIST1 proteins, showing the regions needed for their interaction (arrows), and the position of their MIMs.