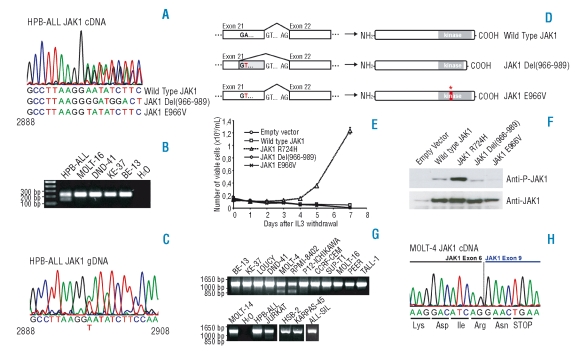
Figure 1.
Analysis of JAK1 sequence variants detected in T-ALL cell lines. (A) Chromatogram corresponding to the JAK1 transcript in the HPB-ALL cell line indicating the presence of wild type JAK1 and two variant transcripts. (B) RT-PCR performed with primers in exon 21 and 22 confirms the presence of an alternative transcript in HPB-ALL. (C) Genomic DNA sequence of JAK1 in the HPB-ALL cell line reveals a 2897A>T substitution. (D) Scheme illustrating the mechanism for generating the observed transcript variant in the HPB-ALL cell line. (E) Proliferation of Ba/F3 cells expressing the indicated constructs in absence of IL3 (IL3 was removed at day 0). JAK1 Wild Type, R724H, Del(966–989) and E966V cDNA sequences were amplified by PCR from T-ALL cell lines and cloned into the pMSCV-GFP vector. All constructs were verified by sequencing. Data are presented as mean ± st dev. (F) Western blots illustrating that only the JAK1(R724H) mutant displays increased JAK1 phosphorylation as compared to wild type JAK1 when overexpressing the indicated constructs in HEK293T cells. (G) RT-PCR in T-ALL cell lines with primers amplifying the 5’ region of JAK1 reveals the presence of shorter JAK1 transcripts in the MOLT-4 and RPMI-8402 cell lines. (H) Chromatogram representing the sequence of the 850 bp band amplified from cDNA of the MOLT-4 cell line that is shown in part G. of this figure. The chromatogram shows fusion of exon 6 and 9, resulting in frame-shift and premature stop-codon formation.