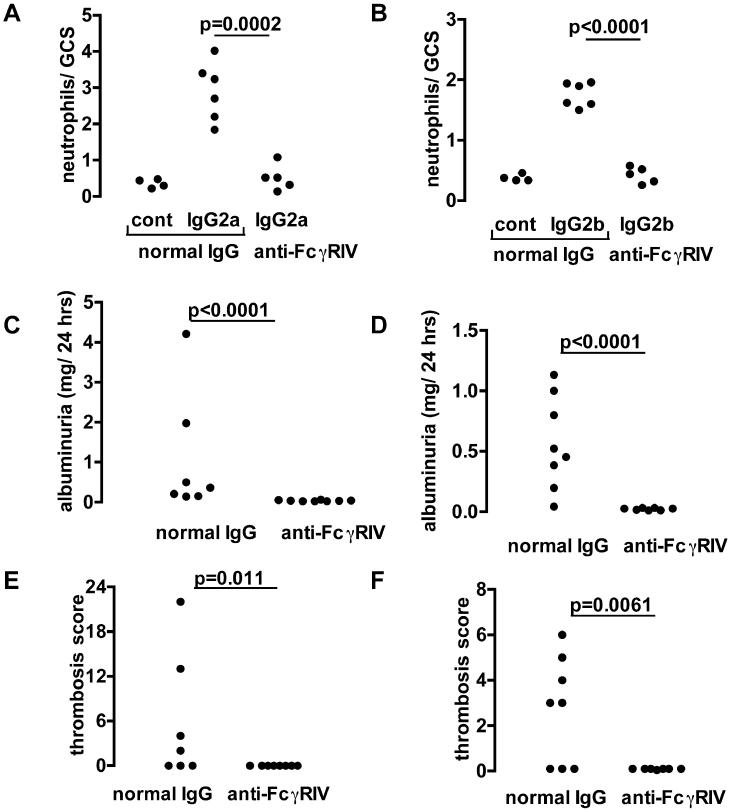
Figure 9.
The role of FcγRIV in IgG2a and IgG2b induced disease. A. Numbers of neutrophils infiltrating glomeruli 2 hours after IgG2a anti-TNP monoclonal with endotoxin, given 24 hours after an intravenous injection of TNP conjugated nephrotoxic antibody, and 90 minutes after 20mg/kg of anti-FcγRIV or control antibody. The control group (left group of each graph) is wildtype mice given normal hamster IgG in the second injection and endotoxin alone in the third injection. B. Shows a similar experiment in which disease was induced by IgG2b anti-TNP. For both IgG2a and IgG2b induced disease, there were significantly less neutrophils in mice given anti-FcγRIV antibody compared to control, with neutrophil numbers reduced to those seen after endotoxin alone. C. Albuminuria in disease induced by IgG2a with endotoxin, was significantly less after anti-FcγRIV compared to control antibody. D. Albuminuria in disease induced by IgG2b with endotoxin was significantly less after anti-FcγRIV compared to control antibody. E. Quantitation of the glomerular thrombosis induced by IgG2a, with results that mirror those for albuminuria. F. Thrombosis was also decreased by anti-FcγRIV antibody in IgG2b-induced disease.