Fig. 1.
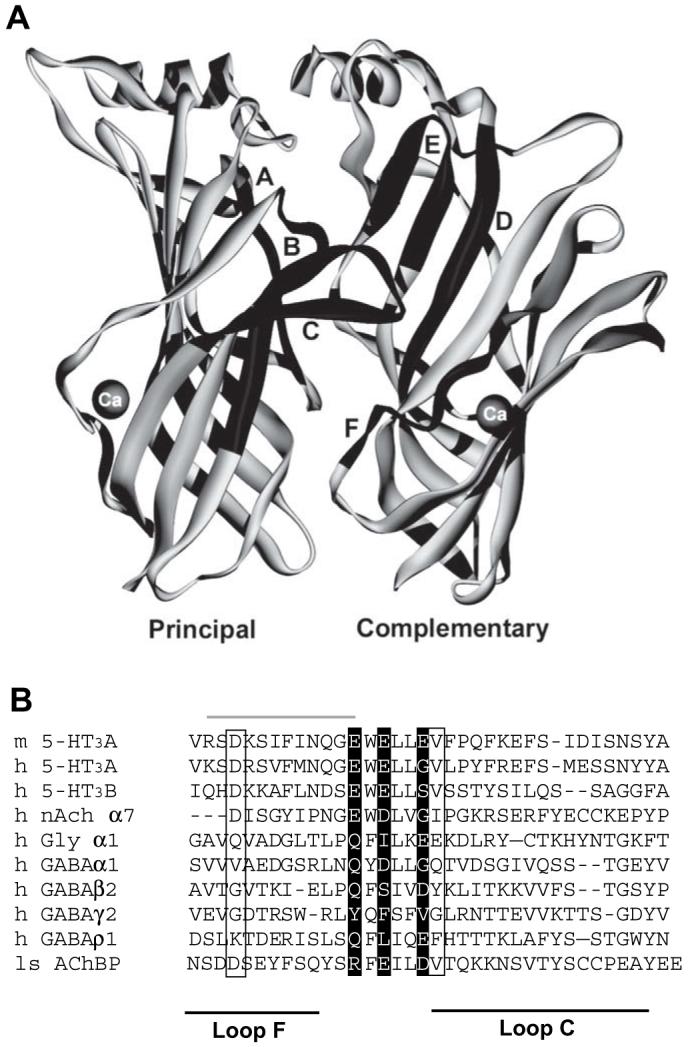
Location of two potential calcium binding sites in the 5-HT3 extracellular domain. (A) The original AChBP structure (1i9b) with Ca2+ coordinated by the side chains of D161 and D175, and the backbone carbonyl of V176. Only two of the five subunits are shown for clarity. The six loops (A-F) that constitute the binding site are shown in black. (B) An alignment of the AChBP loops C and F with members of the Cys-loop LGIC family. The three glutamate residues of the 5-HT3 consensus calcium binding site are shown as white text on a black background. The three residues from the calcium binding site identified in AChBP are indicated by a box. Note that the two potential binding sites overlap at E218. The region of the 5-HT3 receptor that was exchanged for the corresponding α7 nACh sequence by Galzi et al. (1996) is shown by a grey line above the text.
