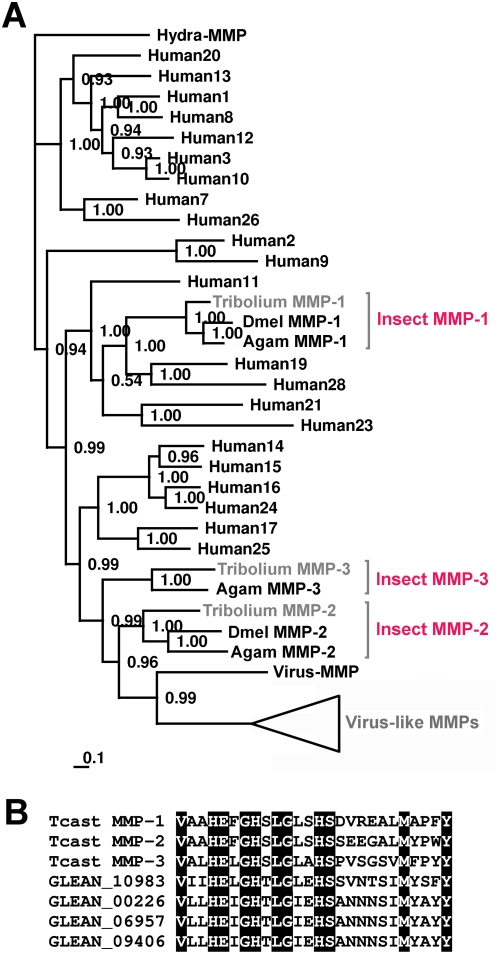
Figure 1. Phylogenetic analysis of Tribolium MMPs along with MMPs from other organisms.
A Bayesian protein tree, with posterior probabilities, was generated using aligned MMP sequences from T. castaneum, Anopheles gambiae, Drosophila melanogaster, Homo sapiens, and Heliothis zea virus 1. A Hydra vulgaris MMP was used as outgroup. This analysis revealed that Tribolium MMP-1 is orthologous to other insect MMP-1s and Tribolium MMP-2 to MMP-2 from Anopheles and Drosophila. Interestingly, Tribolium MMP-3 clades with MMP-3 from Anopheles, but a MMP-3 orthologue is obviously absent in Drosophila. Insect MMP-1 proteins show highest relation to human MMP-19 and MMP-28 whereas the other insect MMPs group together with human membrane-anchored MMPs (MMP-14 to MMP-17, MMP-24 and MMP-25). In contrast to Anopheles and Drosophila, Tribolium has numerous genes that are most closely related to a MMP from Heliothis zea virus 1. The scale bar represents the substitutions per site according to the model of amino acid evolution applied. (B) Three Tribolium MMPs and virus-derived Tribolium MMP proteins have catalytic domains with conserved MMP specific active site sequences (MMP active site consensus sequence: HEXGHXXGXXHSX6M). For better overview sequences of only four virus-derived MMPs are shown.