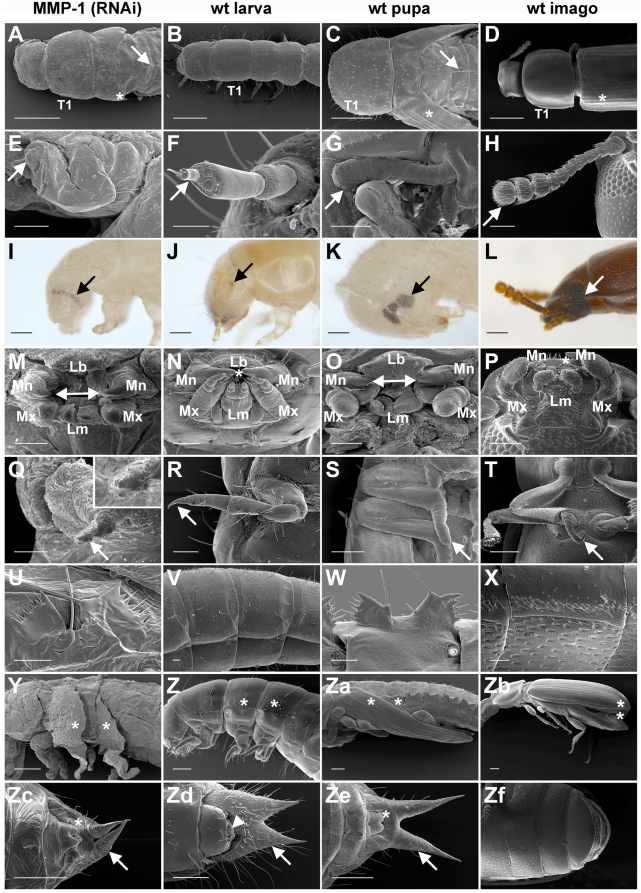
Figure 4. MMP-1 knock-down phenotype.
MMP-1 knock-down animals were analyzed in detail in comparison to wild-type larva, pupa and imago. (A–D) MMP-1 knock-down animals had early pupa-like dorsal features including thorax segment 1 (T1), wings (asterisks) and a pupa-specific abdominal line of setae (arrows). (E–H) Their antennae were thick and un-segmented (tips of antennae are indicated by arrows). (I–L) MMP-1 (RNAi) larvae displayed premature compound eyes (pupal ommatidia) and exhibited reduced larval stemmata (arrows). (M–P) The mouth of MMP-1 (RNAi) phenotype animals exhibited a pupa-like morphology; mandible (Mn), maxilla (Mx), labrum (Lb), labium (Lm), gap between mandibles (indicated by arrow lines in pupa and MMP-1 knock-down phenotype), interlocking of mandibles (indicated by asterisks in larva and imago). (Q–T) MMP-1 (RNAi) larvae had shortened legs with a double inchoate claw similar to that observed in pupa (tip of legs are indicated by arrows). (U–X) Gin-traps were present in MMP-1 knock-down animals and pupae but were absent in wild-type larvae and imagoes. (Y–Zb) In MMP-1 (RNAi) animals wings were rudimentally developed (asterisks) (Zc–Zf), but genital papillae (asterisks, covered in adults) developed into those of pupae, replacing larval pygopods (arrow-head). Furthermore, urogomphi were elongated and pupa-like (arrows, not present in imago). Scale bars: A–D, 500 µm; E–H and M–T, 100 µm; I–L and Y–Zf, 200 µm; U–X, 50 µm.