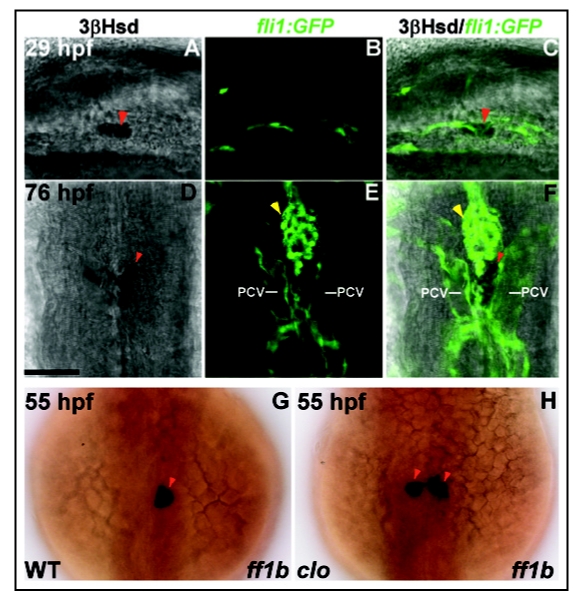
Figure 3.
(A–F) Interaction of interrenal and endothelial cells as revealed in Tg(fli1:EGFP)Y1 transgenic zebrafish. Single confocal sections showing the interrenal tissues as stained by 3β-Hsd activity assay (left panel: A and D), and the neighboring ECs as labeled by the green fluorescence (middle panel: B and E), of the Tg(fli1:EGFP)Y1 embryos while staged at 29 hpf (A–C) and 76 hpf (D–F) respectively. The merged images of 3β-Hsd activity and GFP are shown in the right panel (C and F). (A–C) are lateral views with anterior oriented to the right. (D–F) are dorsal views with anterior oriented to the top. The interrenal cells are in close contact with ECs that are engaged in axial vessel assembly. PCV, posterior cardinal vein. Red arrowheads indicate interrenal tissues, while yellow arrowheads indicate kidney glomeruli. Bar, 50 µM. (G and H) ff1b expression in the clom39 mutant and its wild type sibling. Embryos of clom39 mutant (H) and its wild-type sibling (WT; G) were labeled by in situ hybridization for ff1b (dark blue) at 55 hpf. Dorsal views of embryos are shown, with anterior oriented to the top. The central migration of interrenal tissue is arrested in clom39, resulting in persistent distribution of a pair of cell clusters on either side of midline. Reproduced with permission.20