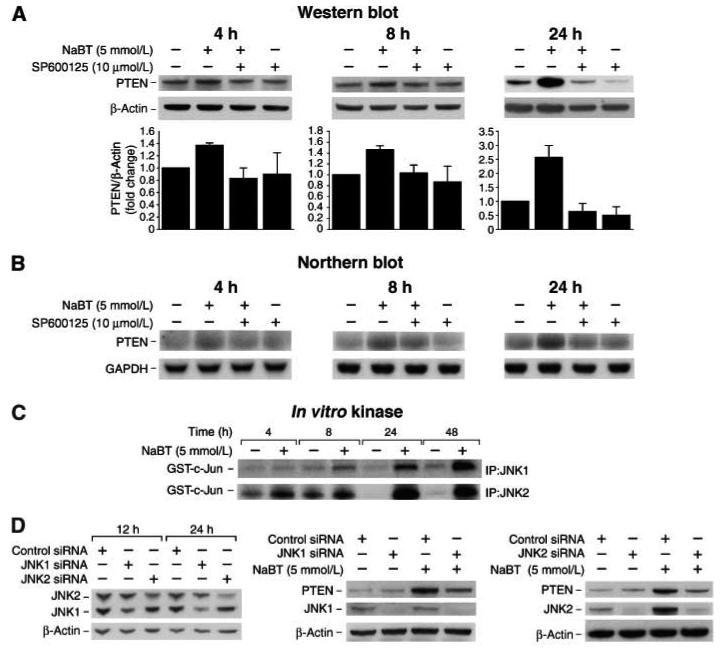
Fig. 2. NaBT-induced PTEN expression requires JNK activation.
A. HT29 cells were pretreated with a specific JNK inhibitor, SP600125, for 30 min followed by treatment with NaBT for 4, 8 or 24 h. Total protein was extracted and Western blot was performed for analysis of PTEN protein expression. B. HT29 cells were pretreated with a specific JNK inhibitor, SP600125, for 30 min followed by treatment with NaBT for 4, 8 or 24 h. Total RNA was extracted and Northern blot was performed for analysis of PTEN mRNA expression. C. HT29 cells were treated with NaBT from 4 to 48 h. Whole cell protein was extracted for immunoprecipitation using anti-JNK1 or JNK2 antibody. JNK1 and JNK2 activity was assessed by an in vitro kinase assay using GST-c-Jun protein as substrate. D. HT29 cells were transfected with siRNA directed to JNK1 or JNK2 or control siRNA. Cells were harvested 12 or 24 h after transfection (left) or 24 h after transfection, cells were treated with NaBT for an additional 24 h (middle & right). Whole cell protein was extracted and Western blot was performed for analysis of PTEN protein expression. Knockdown of either JNK1 or JNK2 attenuated PTEN induction by NaBT. PTEN signals from three separate experiments were quantitated densitometrically and expressed as fold-change with respect to β-actin.