Figure 24.1.
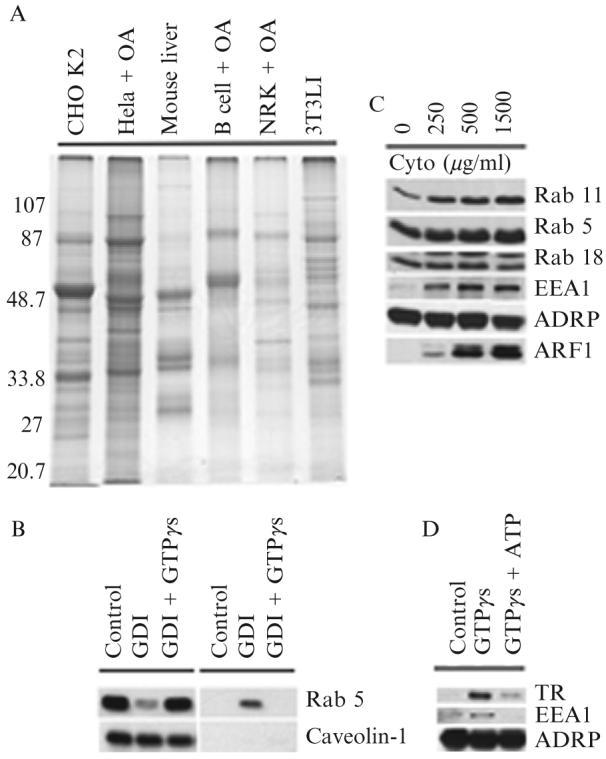
(A) Signature protein of adiposomes from different cells. Adiposomes were purified from the indicated cells grown in the presence or absence of oleic acid (OA). Proteins were precipitated with 100% acetone and dissolved in SDS sample buffer, and 10 μg of proteins was separated on 10% SDS-PAGE and stained with Coomassie colloidal blue. Adiposomes were isolated from 3T3 L1 cells after 8 days of differentiation. (B) Release of GDP-bound Rab 5 from adiposomes by RabGDI. Purified adiposomes were incubated in the presence of RabGDI (GDI) plus or minus GTPγs. Adiposomes (left) and reaction buffer (right) were separated and processed for immunoblotting to detect the indicated proteins. (C) Recruitment of Rabs from cytosol to adiposome. Purified adiposomes were processed to remove endogenous Rabs with RabGDI. Rab-depleted adiposomes were then incubated with the indicated concentrations of cytosol for 1 h. At the end of the reaction, adiposomes were reisolated, washed, and processed for immunoblotting to detect the indicated proteins. The adiposome-specific protein ADRP was used as a loading control. (D) Early endosomes bind adiposomes. Purified adiposomes were mixed with purified early endosomes in the presence or absence of GTPγs and ATP. Adiposomes were reisolated and unbound endosomes removed. Adiposomes were then processed for immunoblotting to detect the indicated proteins. ADRP was used as a loading control.TR, transferrin receptor.
