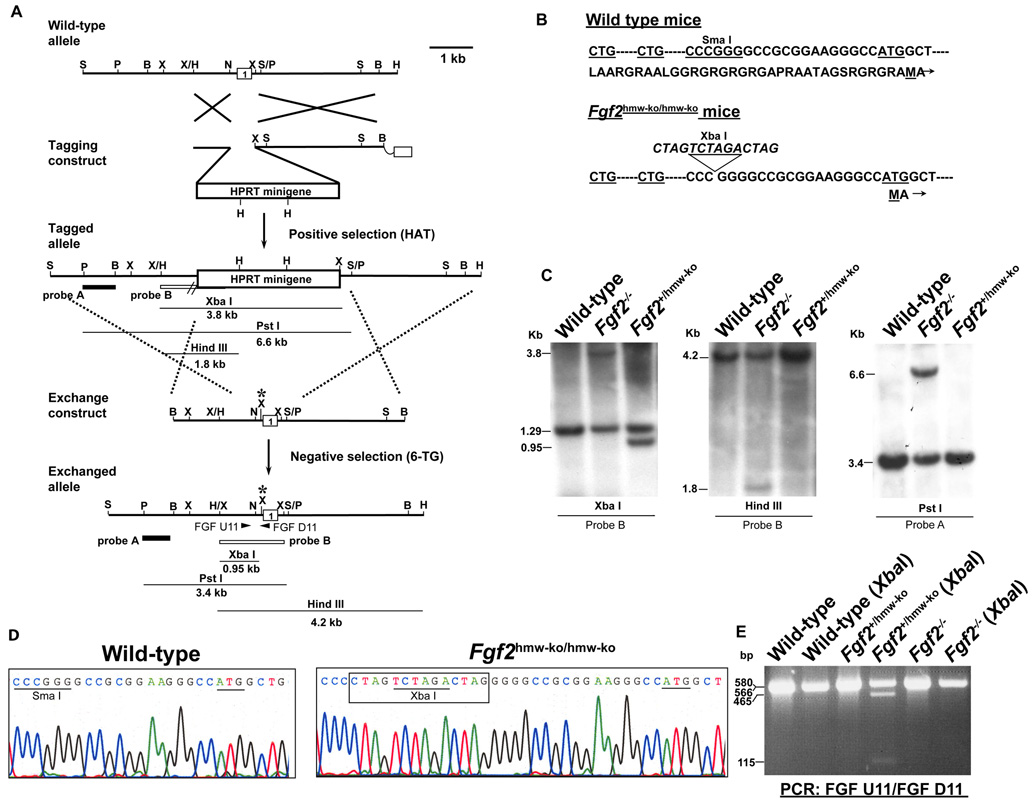
Figure 1. Generation of Fgf2hmw-ko/hmw-ko mice.
(A) Tag and Exchange gene targeting strategy and resulting Fgf2hmw-ko exchanged allele. (B) DNA and protein sequence of wildtype and FGF2 HMW KO mice. A 14 bp Oligo containing a XbaI site is inserted into Sma I site located 5’ upstream of canonical ATG start codon. (C) Southern blot analyses showing mice carrying wild type alleles and knockout alleles (Fgf2−/−), and a germline chimeric mouse carrying a successfully targeted exchanged allele (Fgf2+/hmw-ko). (D) DNA sequencing of genomic PCR products indicating the presence of 14 bp Oligo with a XbaI site and the intact canonical ATG start codon in FGF2 HMW KO mice. (E) PCR Genotyping of germline chimera. Restriction enzyme digestion indicates the presence of a functional XbaI site in the Fgf2hmw-ko allele in the germline chimera. Notably, difference in band intensities on this blot is due to unequal loading of protein samples in different lanes. Probes and the expected band size for Southern analysis are indicated in (A). Long arrows in (A) represent MFGF U1 (Forward) and PGK D1 (Reverse) PCR primers used to identify the Hprt-tagged allele; arrowheads in (A: Exchanged allele) represent FGF U11 (forward) and FGF D11 (reverse) primers used to identify the targeted exchanged allele. Asterisk in exchange construct and exchanged allele indicates the presence of 14 bp Oligo and XbaI site. B, BamHI; H, HindIII; N, NarI; P, PstI; S, SacI; Sm, SmaI; X, XbaI.