Figure 1.
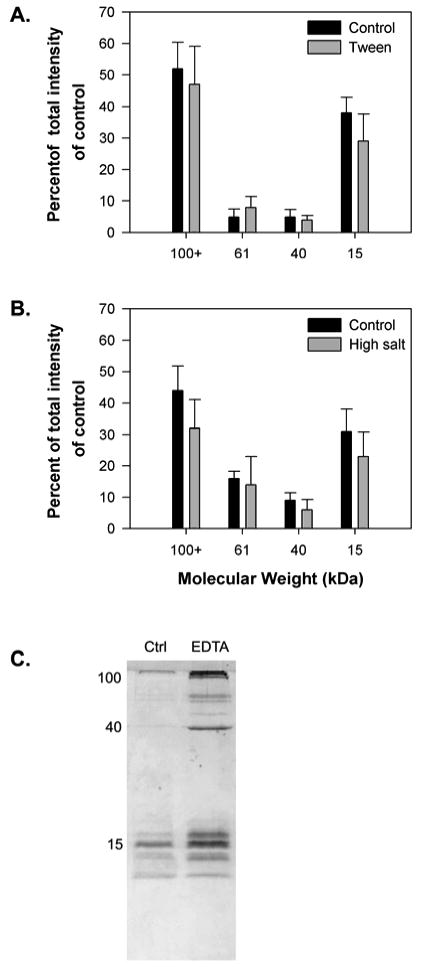
The effect of disrupting hydrophobic interactions, disrupting electrostatic interactions, and removing divalent ions on the solubility of glue from the slug A. subfuscus. A+ B) Quantitative analysis of the effect of the non-ionic detergent Tween-20 (0.5%) and high salt concentration (1 M NaCl) respectively. The bars in A and B show the staining intensity of bands on SDS-PAGE for the four most common proteins in the glue. Band intensities are expressed as a percentage of the total staining intensity of all four bands in the control. Several proteins of greater than 100 kDa are pooled together. The results for each show the mean ± S.D. of three trials dissolved using the same procedure. C) SDS-PAGE showing the effect of divalent ion chelation (10 mM EDTA). The position of three major bands at 15, 40 and 100 kDa is shown on the left.
