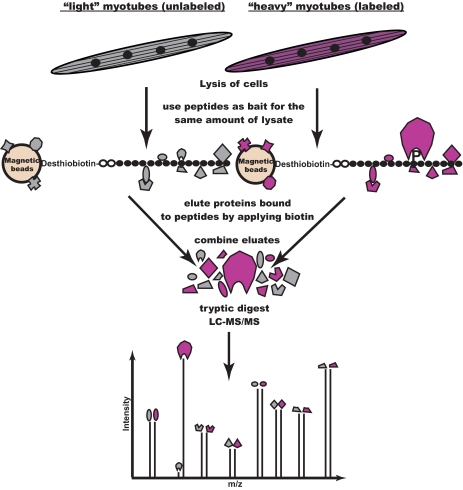
Fig. 1.
Proteomic screening for interaction partners of tyrosine phosphorylated sequences. Peptides corresponding to potential tyrosine phosphorylation sites are synthesized in phosphorylated and non-phosphorylated form. Cell populations are metabolically labeled using the SILAC technique to allow discrimination based on different peptide masses. Cell lysate from the population labeled with heavy Arg and Lys is incubated with the phosphorylated version of the peptide, whereas the control cell lysate is incubated with the non-phosphorylated peptide. Eluted proteins from those parallel pulldown experiments are combined and digested with trypsin. Peptides from unspecific background binders appear as pairs with abundance ratios close to 1:1 in the mass spectra. Phosphorylation-specific binders are identified as such through their high abundance ratio between heavy and light labeling states. In a crossover experiment, the incubation scheme is swapped, resulting in inverted ratios.