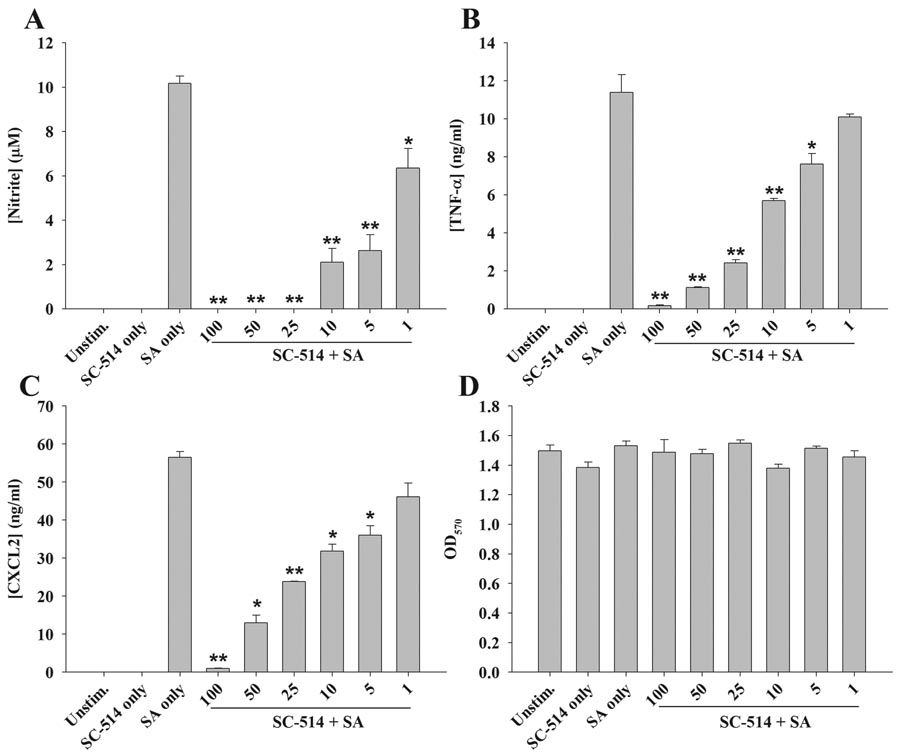
Figure 2. The IKK inhibitor SC-514 attenuates astrocytic proinflammatory mediator release in response to S. aureus.
Primary astrocytes were seeded in 96-well plates at 1 × 105 cells per well and incubated overnight. The following day, cells were pre-treated for 1 h with the indicated concentrations of SC-514 (1–100 µM) followed by stimulation with 107 colony forming units (cfu) of heat-inactivated S. aureus (SA). Cell-free supernatants were collected at 24 h following bacterial exposure and analyzed for nitrite (A), TNF-α (B), and CXCL2 (C) production. Astrocyte viability was assessed using a standard MTT assay and the raw OD570 absorbance values are provided (D). Results are reported as the mean ± SD of three independent wells for each experimental treatment. Significant differences between S. aureus-stimulated astrocytes versus S. aureus + SC-514 are denoted with asterisks (*, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.001). Results are representative of two independent experiments.