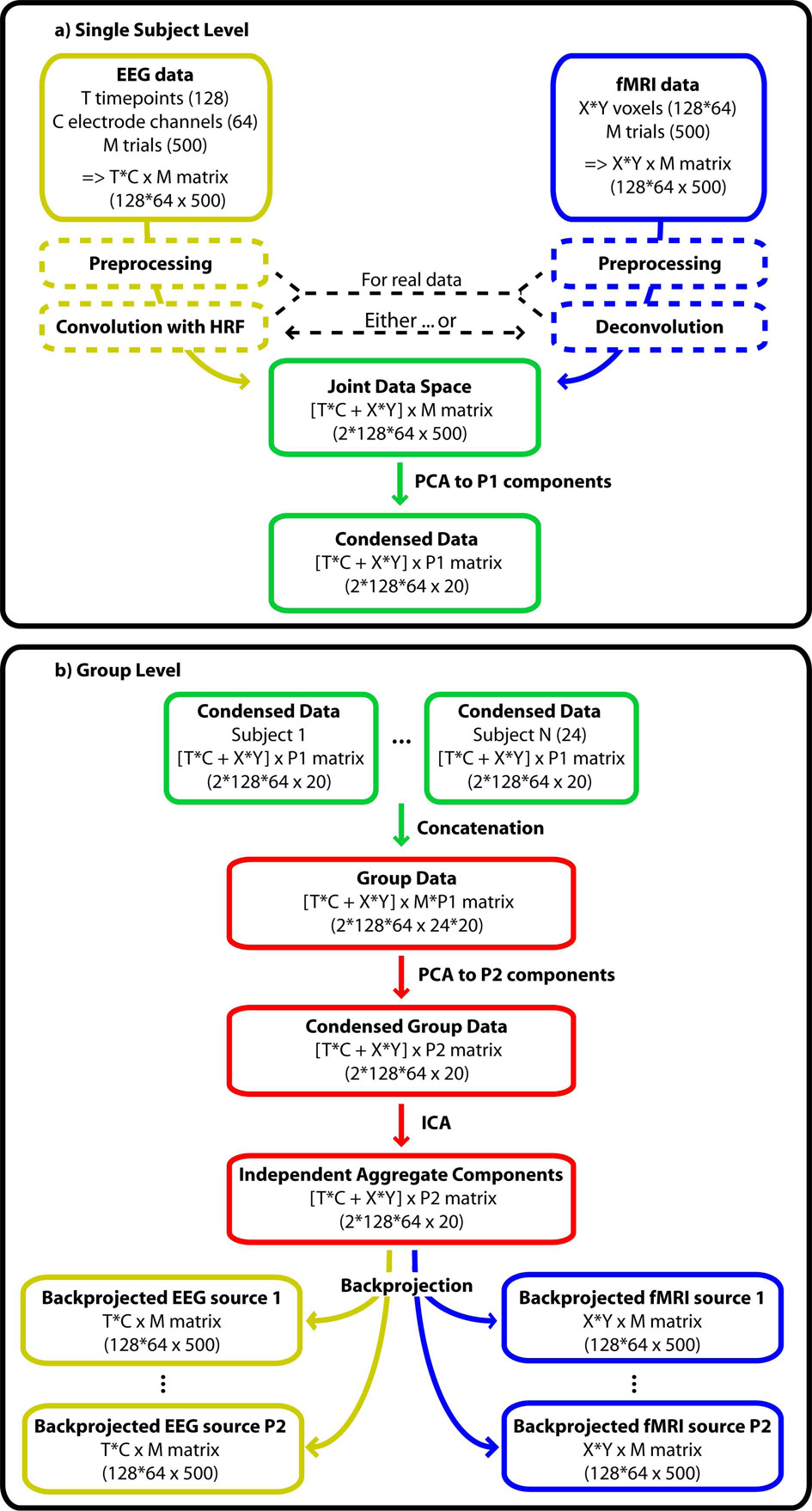
Figure 1.
Schematic illustration of the joint ICA approach. EEG and fMRI data should undergo typical preprocessing, including convolution or deconvolution to compensate for the hemodynamic lag before entering the joint data space. A PCA compresses the data on single subject level. Single subject data are then concatenated in an aggregate set. A second PCA condenses redundant information on group level before the data are decomposed into independent components. Backprojection to EEG and fMRI data space allows the visualization of the separated processes. The numbers in brackets specify the matrix dimension chosen in this simulation. The symbol ‘x’ denotes ‘by’ as in a 10 by 20 matrix whereas the symbol ‘*’ denotes multiplication.