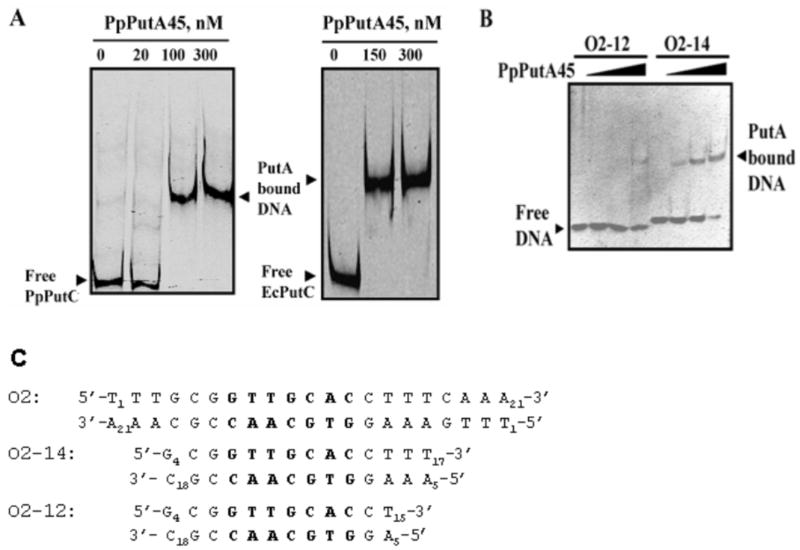
Fig. 3.
Gel-mobility shift assays of PpPutA45. A, Gel-shift assays in which increasing concentrations of PpPutA45 were added to binding mixtures containing IRdye-700 labeled put intergenic DNA (2 nM) from P. putida (PpPutC) or E. coli (EcPutC) and 100 μg/ml of nonspecific calf thymus DNA at 23 °C. B, Gel-shift assays of PpPutA45 with O2-12 and O2-14. Double stranded O2-12 and O2-14 (100 nM) were incubated with increasing concentrations of PpPutA45 (0 – 400 nM) in 20 mM potassium phosphate buffer (pH 7.4, 100 mM NaCl). The protein-DNA complexes were then separated using a nondenaturing polyacrylamide gel (8%) native gel at 4 °C. C, Nucleotide sequence of the O2 site from E. coli put intergenic DNA and the 14-bp (O2-14) and 12-bp (O2-12) oligomers used in panel B for the gel-shift analysis. Oligomer O2-14 was used for the NMR studies of the PpPutA45-DNA complex. Highlighted in bold is the base pair region that makes contacts with PutA residues in the PpPutA45-DNA structure.