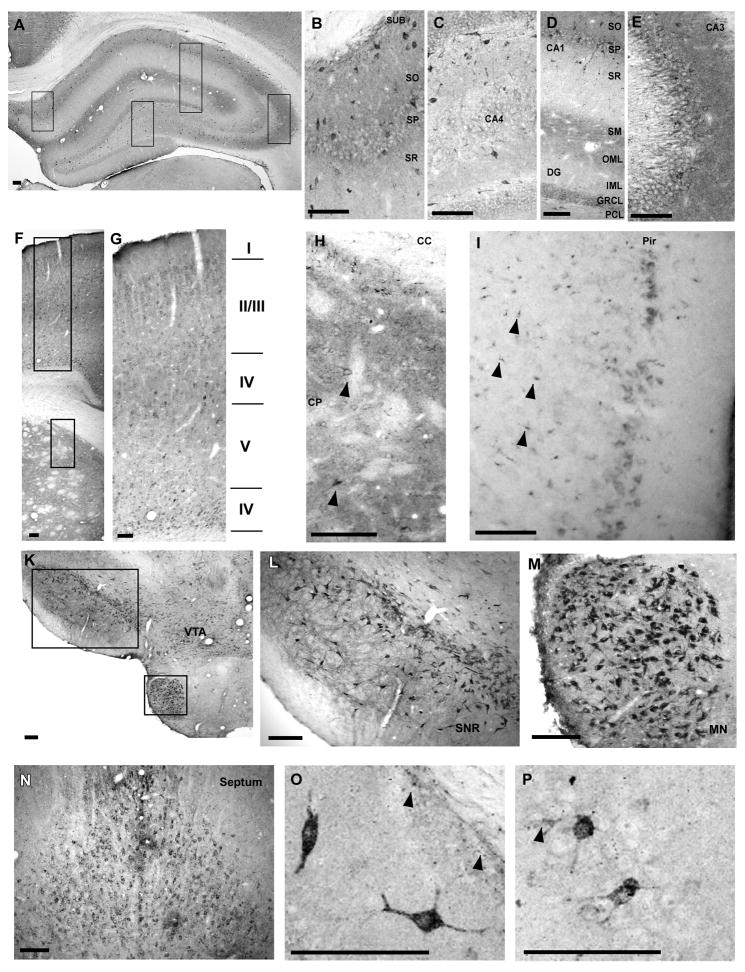
Fig. 1.
Regional distribution of cypD within different brain regions. Hippocampus (A–E). The intensity of staining within the cellular layers is highest in CA3 (E) followed by subicculum (B), CA1 and dentate gyrus (D). Furthermore, the immunoreactivity is particularly high above and below the hippocampal fissure and within the cellular and basal dendritic layers of CA3. There are scattered cells with intense staining throughout all hippocampal regions. Panels B–E are enlarged images taken from panel as shown by black boxes. Caudate putamen and overlaying cortex (F–H). Intense immunoreactivity within caudate putamen with scattered strongly stained neurons (arrowheads) (H). Strongly stained neurons are localized particularly in cortical layers II/IV and VI (G). Neurons with high cypD immunoreactivity were also localized in layer I of Piriform cortex. Furthermore, non-neuronal cells in deeper layers within this region were also strongly stained (arrowheads). Substantia nigra (SNr), ventral tagmental area (VTA), mammilary nucleus (MN) (K, L, M) and septum (N) contained neurons with intense staining. Panel O and P demonstrate individual neurons within the CA1 (O) and the CA3 (P) sector of the hippocampus with high immunoreactivity. Arrowheads indicate non-neuronal cells with high cypD staining. Scale bar = 100 μm.