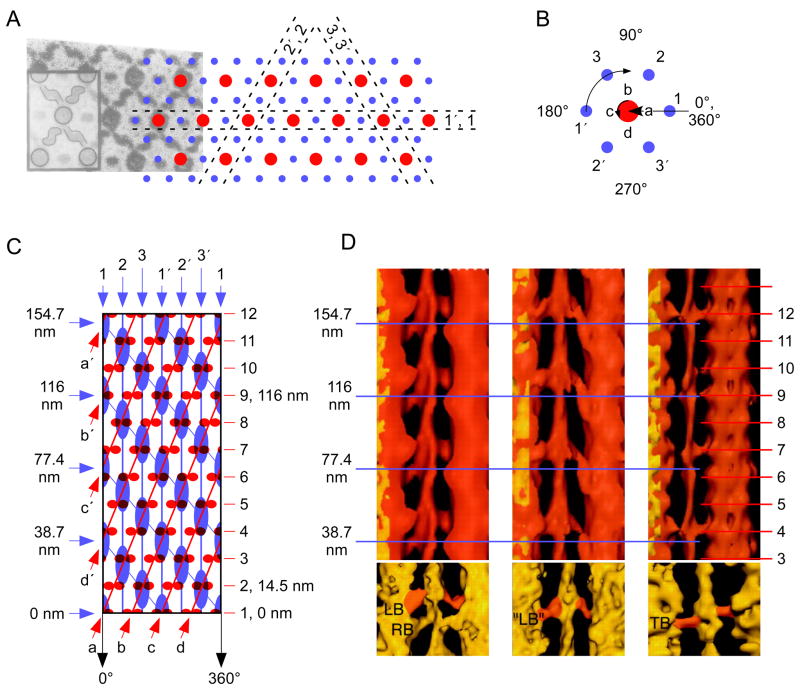
Figure 7.
Thin and thick filament organization and interactions in Lethocerus asynchronous flight muscle. A. Electron micrograph of cross section through muscle (left portion) merging into a schematic of thick (red circles) and thin (blue circles) filaments. Corridors defined by dashed lines mark thin filaments that are in helical register; all thick filaments are also in helical register. Cross bridges are apparent in electron micrograph, inset schematically shows different cross bridge shapes. B. Single thick filament (red circle) and its surrounding thin filaments (small circles). Letters on thick filament indicate head origins, arrow indicates that the filament is right handed. Numbers indicate pairs of thin filaments that are in helical register. Arrow indicates left handed helix of preferred binding sites, helix rotates 60° with each thin filament. C. Spatial relationship between myosin heads (small red ellipses) and thin filament preferred binding sites (large blue ellipses). ‘Unrolled’ and laid flat representation of the arrangement shown in panel B rotated so that the thin filaments (thick vertical blue lines, numbers and blue arrows on top of box) lie in the plane of the figure. Myosin heads leave the thick filament every 14.5 nm, actin helices (leftward slanted thin blue lines) repeat every 38.7 nm (blue arrows, numbers on left of box), preferred thin filament binding sites repeat every 12.9 nm. The thin rightward slanting red lines labeled ‘a–d’ are the right handed helices connecting myosin heads; letters with primes show continuation of helices that have ‘run off’ the right side of the box. D. Average (top panels) and representative individual (bottom panels) three dimensional electron micrograph reconstructions of two thick filaments and an interposed thin filament in rigor (left panels) and pharmacological treatments that reduce thick:thin filament binding (middle and right panels). Numbered red lines on right represent shelf positions, numbered blue lines on left preferred binding sites on the thin filament. In each case lines exactly correspond to those in panel C. Modified from Reedy and Reedy (1985) (A), Wray (1979a) and Schmitz et al. (1994a) (C), and Schmitz et al. (1997) (D).